|
| fsp_err_t | R_RMAC_PHY_Open (ether_phy_ctrl_t *const p_ctrl, ether_phy_cfg_t const *const p_cfg) |
| | Resets Ethernet PHY device. Implements ether_phy_api_t::open. More...
|
| |
| fsp_err_t | R_RMAC_PHY_Close (ether_phy_ctrl_t *const p_ctrl) |
| | Close Ethernet PHY device. Implements ether_phy_api_t::close. More...
|
| |
| fsp_err_t | R_RMAC_PHY_StartAutoNegotiate (ether_phy_ctrl_t *const p_ctrl) |
| | Starts auto-negotiate. Implements ether_phy_api_t::startAutoNegotiate. More...
|
| |
| fsp_err_t | R_RMAC_PHY_LinkPartnerAbilityGet (ether_phy_ctrl_t *const p_ctrl, uint32_t *const p_line_speed_duplex, uint32_t *const p_local_pause, uint32_t *const p_partner_pause) |
| | Reports the other side's physical capability. Implements ether_phy_api_t::linkPartnerAbilityGet. More...
|
| |
| fsp_err_t | R_RMAC_PHY_LinkStatusGet (ether_phy_ctrl_t *const p_ctrl) |
| | Returns the status of the physical link. Implements ether_phy_api_t::linkStatusGet. More...
|
| |
| fsp_err_t | R_RMAC_PHY_ChipInit (ether_phy_ctrl_t *const p_ctrl, ether_phy_cfg_t const *const p_cfg) |
| | Initialize Ethernet PHY device. Implements ether_phy_api_t::chipInit. More...
|
| |
| fsp_err_t | R_RMAC_PHY_Read (ether_phy_ctrl_t *const p_ctrl, uint32_t reg_addr, uint32_t *const p_data) |
| | Read data from register of PHY-LSI . Implements ether_phy_api_t::read. More...
|
| |
| fsp_err_t | R_RMAC_PHY_Write (ether_phy_ctrl_t *const p_ctrl, uint32_t reg_addr, uint32_t data) |
| | Write data to register of PHY-LSI . Implements ether_phy_api_t::write. More...
|
| |
| fsp_err_t | R_RMAC_PHY_ChipSelect (ether_phy_ctrl_t *const p_ctrl, uint8_t port) |
| | Update the target PHY LSI of this driver. More...
|
| |
| fsp_err_t | R_RMAC_PHY_CallbackSet (ether_phy_ctrl_t *const p_ctrl, void(*p_callback)(ether_phy_callback_args_t *), void *const p_context, ether_phy_callback_args_t *const p_callback_memory) |
| |
The RMAC PHY module (r_rmac_phy) provides an API for standard Ethernet PHY communications applications that use the RMAC peripheral. It implements the Ethernet PHY Interface.
Overview
The RMAC PHY module is used to setup and manage an external Ethernet PHY device. r_rmac_phy use the on-chip MAC layer peripheral(RMAC), which is part of Ethernet Switch Module(ESWM). It performs auto-negotiation to determine the optimal connection parameters between link partners. Once initialized the connection between the external PHY and the onboard controller is automatically managed in hardware.
The following figure shows which IPs are used by the r_rmac_phy module.
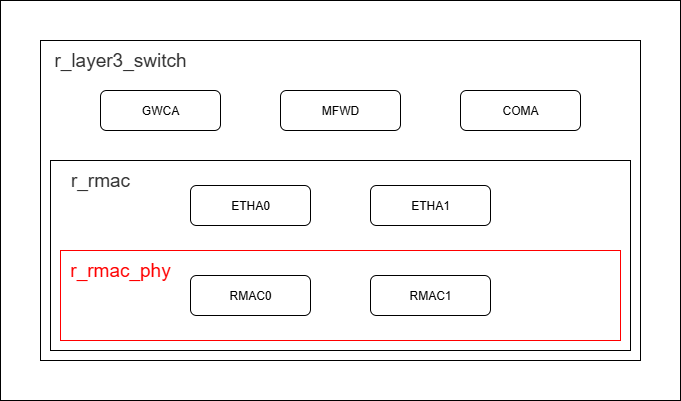
ESWM block diagram
Features
The RMAC PHY module supports the following features:
- Auto negotiation support
- Flow control support
- Link status check support
- Gigabit Ethernet support
Following features are not supported:
- Extensions to management frame format defined in IEEE802.3 clause 45
Supported Devices
| Device Group | Devices |
| RA8 | RA8D2, RA8M2, RA8P1, RA8T2 |
Configuration
Build Time Configurations for r_rmac_phy
The following build time configurations are defined in fsp_cfg/r_rmac_phy_cfg.h:
| Configuration | Options | Default | Description |
| Parameter Checking |
-
Default (BSP)
-
Enabled
-
Disabled
| Default (BSP) | If selected code for parameter checking is included in the build. |
| KSZ8091RNB Target |
| Disabled | Select whether to use KSZ8091RNB PHY-LSI or not. |
| KSZ8041 Target |
| Disabled | Select whether to use KSZ8041 PHY-LSI or not. |
| DP83620 Target |
| Disabled | Select whether to use DP83620 PHY-LSI or not. |
| ICS1894 Target |
| Disabled | Select whether to use ICS1894 PHY-LSI or not. |
| GPY111 Target |
| Disabled | Select whether to use GPY111 PHY-LSI or not. |
| VSC8541 Target |
| Disabled | Select whether to use VSC8541 Phy LSI or not. |
| User Own Target |
| Disabled | Select whether to use User own Phy LSI or not. |
| Reference Clock |
| Default | Select whether to use the RMII reference clock. Selecting 'Default' will automatically choose the correct option when using a Renesas development board. |
| Reference Clock |
| Default | Select whether to use the RMII reference clock. Selecting 'Default' will automatically choose the correct option when using a Renesas development board. |
Configurations for Networking > Ethernet (r_rmac_phy)
This module can be added to the Stacks tab via New Stack > Networking > Ethernet (r_rmac_phy). Non-secure callable guard functions can be generated for this module by right clicking the module in the RA Configuration tool and checking the "Non-secure Callable" box.
| Configuration | Options | Default | Description |
| Interrupts |
| Context | Name must be a valid C symbol | NULL | Placeholder for user data. Passed to the user callback in ether_switch_callback_args_t. |
| Callback | Name must be a valid C symbol | NULL | Callback provided when an ISR occurs |
| ETHA0 status interrupt priority | MCU Specific Options | | Select the ETHA0 status interrupt priority. |
| ETHA1 status interrupt priority | MCU Specific Options | | Select the ETHA1 status interrupt priority. |
| Name | Name must be a valid C symbol | g_rmac_phy0 | Module name. |
| Channel |
| 0 | Select the Ethernet controller channel number. |
| Default PHY-LSI port |
| 0 | Specify the default port for PHY-LSI configuration. |
| PHY-LSI Reset Completion Timeout | Specify a value between 0x1 and 0xFFFFFFFF. | 0x00020000 | Specify the number of times to read the PHY-LSI control register while waiting for reset completion. This value should be adjusted experimentally based on the PHY-LSI used. |
| Select MII type |
| RMII | Specify whether to use MII or RMII. |
| Port Custom Init Function | Name must be a valid C symbol | NULL | Set the initial function of the PHY-LSI, When using your own PHY-LSI. |
| Port Custom Link Partner Ability Get Function | Name must be a valid C symbol | NULL | Set the link partner ability get function of the PHY-LSI, When using your own PHY-LSI. |
| Flow Control |
| Disable | Select whether to enable or disable flow control. |
| Management frame format | Clause 22 frame format | Clause 22 frame format | Select the management frame format used to access the PHY-LSI. |
| MDC clock rate (Hz) | Value must be a non-negative number | 2500000 | Specify the MDC clock frequency |
| MDIO hold timing adjustment | Value must be a non-negative integer less than 8 | 0 | Specify the clock cycle for hold timing. |
| MDIO capture timing adjustment | Value must be a non-negative integer less than 8 | 0 | Specify the clock cycle for capture timing. |
| Frame preemption |
| Disable | Select whether to enable or disable frame preemption feature. |
| Verify frame interval | Value must be a non-negative integer less than 128 | 10 | Interval for sending verify frame [ms]. |
Usage Notes
Accessing the Registers in PHY-LSI
Use the RMAC peripheral to access the registers in the PHY-LSI. Management frame is transmitted and received through the ETn_MDC and ETn_MDIO pins controlled by hardware.
This HW supports two management frame format.
- Normal management frame format defined in Clause 22 of IEEE802.3 (Describe “MDIO” in this document)
- Extension management frame format defined in Clause 45 of IEEE802.3 (Describe “eMDIO” in this document)
Management frame format of MDIO (Clause 22)
The below table lists the management frame formats of MDIO.
| Access type | MII and RMII management frame |
| Item | PRE | ST | OP | PHYAD | REGAD | TA | DATA | IDLE |
| Number of bits | 32 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 5 | 2 | 16 | 1 |
| Read | 1...1 | 01 | 10 | 00001 | RRRRR | Z0 | DDDDDDDDDDDDDDDD | Z |
| Write | 1...1 | 01 | 01 | 00001 | RRRRR | 10 | DDDDDDDDDDDDDDDD | Z |
- Note
- - PRE (preamble): Send 32 consecutive 1s.
-
- ST (start of frame): Send 01b.
-
- OP (operation code): Send 10b for read or 01b for write.
-
- PHYAD (PHY address): Up to 32 PHY-LSIs can be connected to one MAC. PHY-LSIs are selected with these 5 bits. When the PHY-LSI address is 1, send 00001b.
-
- REGAD (register address): One register is selected from up to 32 registers in the PHY-LSI. When the register address is 1, send 00001b.
-
- TA (turnaround): Use 2-bit turnaround time to avoid contention between the register address and data during a read operation.
-
Send 10b during a write operation. Release the bus for 1 bit during a read operation (Z is output).
-
(This is indicated as Z0 because 0 is output from the PHY-LSI on the next clock cycle.)
-
- DATA (data): 16-bit data. Sequentially send or receive starting from the MSB.
-
- IDLE (IDLE condition): Wait time before inputting the next MII or RMII management format. Release the bus during a write
-
operation (Z is output). No control is required, because a bus was already released during a read operation.
Management frame format of eMDIO (Clause 45)
The below table lists the management frame formats of eMDIO(Clause 45).
| Access type | MII and RMII management frame |
| Item | PRE | ST | OP | PRTAD | DEVAD | TA | DATA | IDLE |
| Number of bits | 32 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 5 | 2 | 16 | 1 |
| Address | 1...1 | 00 | 00 | PPPPP | EEEEE | 10 | AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA | Z |
| Write | 1...1 | 00 | 01 | PPPPP | EEEEE | 10 | DDDDDDDDDDDDDDDD | Z |
| Read | 1...1 | 00 | 11 | PPPPP | EEEEE | Z0 | DDDDDDDDDDDDDDDD | Z |
| Read Increment | 1...1 | 00 | 10 | PPPPP | EEEEE | Z0 | DDDDDDDDDDDDDDDD | Z |
- Note
- - PRE (preamble): Send 32 consecutive 1s.
-
- ST (start of frame): Send 00b.
-
- OP (operation code): Send 00b for register address, 10b for read operation, 11b for write operation, or 10b for post-read-increment-address operation.
-
- PRTAD (port address): Up to 32 PHY-LSIs can be connected to one MAC. PHY-LSIs are selected with these 5 bits port address. When the port address is 1, send 00001b.
-
- DEVAD (device address): Up to 32 MDIO Manageable Devices(MMD) are contained in a PHY-LSI. MMD are selected with these 5 bits device address.
-
- TA (turnaround): Use 2-bit turnaround time to avoid contention between the register address and data during a read operation.
-
Send 10b during a write operation. Release the bus for 1 bit during a read operation (Z is output).
-
(This is indicated as Z0 because 0 is output from the PHY-LSI on the next clock cycle.)
-
- DATA (data): 16-bit data. Sequentially send or receive starting from the MSB.
-
- IDLE (IDLE condition): Wait time before inputting the next MII or RMII management format. Release the bus during a write
-
operation (Z is output). No control is required, because a bus was already released during a read operation.
Limitations
- The r_rmac_phy module may need to be customized for PHY devices other than the ones currently supported. Use the existing code as a starting point for creating a custom implementation. Supported PHY devices are as follows.
- KSZ8091RNB
- KSZ8041
- DP83620
- ICS1894
- GPY111
- VSC8541
Examples
RMAC PHY Basic Example
This is a basic example of minimal use of the RMAC PHY in an application.
void rmac_phy_basic_example (void)
{
g_rmac_phy0_ctrl.open = 0U;
g_rmac_phy0_cfg.channel = 0;
assert(FSP_SUCCESS == err);
assert(FSP_SUCCESS == err);
{
}
&g_rmac_phy0_line_speed_duplex,
&g_rmac_phy0_local_pause,
&g_rmac_phy0_partner_pause);
assert(FSP_SUCCESS == err);
assert(FSP_SUCCESS == err);
}
◆ rmac_phy_instance_ctrl_t
| struct rmac_phy_instance_ctrl_t |
◆ rmac_phy_extended_cfg_t
| struct rmac_phy_extended_cfg_t |
RMAC PHY extended configuration.
◆ rmac_phy_interface_status_t
Initialization state for read/write
| Enumerator |
|---|
| RMAC_PHY_INTERFACE_STATUS_UNINITIALIZED | ETHER PHY interface is uninitialized.
|
| RMAC_PHY_INTERFACE_STATUS_INITIALIZED | ETHER PHY interface is initialized.
|
◆ rmac_phy_frame_format_t
| Enumerator |
|---|
| RMAC_PHY_FRAME_FORMAT_MDIO | Normal management frame format defined in clause 22.
|
| RMAC_PHY_FRAME_FORMAT_EMDIO | Extension management frame format defined in clause 45.
|
◆ R_RMAC_PHY_Open()
Resets Ethernet PHY device. Implements ether_phy_api_t::open.
- Return values
-
| FSP_SUCCESS | Channel opened successfully. |
| FSP_ERR_ASSERTION | Pointer to RMAC_PHY control block is NULL. |
| FSP_ERR_ALREADY_OPEN | Control block has already been opened or channel is being used by another instance. Call close() then open() to reconfigure. |
| FSP_ERR_INVALID_CHANNEL | Invalid channel number is given. |
| FSP_ERR_INVALID_POINTER | Pointer to p_cfg is NULL. |
| FSP_ERR_INVALID_MODE | Function is called when not in CONFIG mode. |
◆ R_RMAC_PHY_Close()
Close Ethernet PHY device. Implements ether_phy_api_t::close.
- Return values
-
| FSP_SUCCESS | Channel successfully closed. |
| FSP_ERR_ASSERTION | Pointer to RMAC_PHY control block is NULL. |
| FSP_ERR_NOT_OPEN | The control block has not been opened |
| FSP_ERR_INVALID_MODE | Function is called when not in DISABLE mode. |
◆ R_RMAC_PHY_StartAutoNegotiate()
Starts auto-negotiate. Implements ether_phy_api_t::startAutoNegotiate.
- Return values
-
| FSP_SUCCESS | RMAC_PHY successfully starts auto-negotiate. |
| FSP_ERR_ASSERTION | Pointer to RMAC_PHY control block is NULL. |
| FSP_ERR_NOT_OPEN | The control block has not been opened |
| FSP_ERR_NOT_INITIALIZED | The control block has not been initialized |
| FSP_ERR_INVALID_MODE | Function is called when not in OPERATION mode. |
◆ R_RMAC_PHY_LinkPartnerAbilityGet()
| fsp_err_t R_RMAC_PHY_LinkPartnerAbilityGet |
( |
ether_phy_ctrl_t *const |
p_ctrl, |
|
|
uint32_t *const |
p_line_speed_duplex, |
|
|
uint32_t *const |
p_local_pause, |
|
|
uint32_t *const |
p_partner_pause |
|
) |
| |
Reports the other side's physical capability. Implements ether_phy_api_t::linkPartnerAbilityGet.
- Return values
-
| FSP_SUCCESS | RMAC_PHY successfully get link partner ability. |
| FSP_ERR_ASSERTION | Pointer to RMAC_PHY control block is NULL. |
| FSP_ERR_INVALID_POINTER | Pointer to arguments are NULL. |
| FSP_ERR_NOT_OPEN | The control block has not been opened |
| FSP_ERR_ETHER_PHY_ERROR_LINK | PHY-LSI is not link up. |
| FSP_ERR_ETHER_PHY_NOT_READY | The auto-negotiation isn't completed |
| FSP_ERR_NOT_INITIALIZED | The control block has not been initialized |
| FSP_ERR_INVALID_MODE | Function is called when not in OPERATION mode. |
◆ R_RMAC_PHY_LinkStatusGet()
Returns the status of the physical link. Implements ether_phy_api_t::linkStatusGet.
- Return values
-
| FSP_SUCCESS | RMAC_PHY successfully get link partner ability. |
| FSP_ERR_ASSERTION | Pointer to RMAC_PHY control block is NULL. |
| FSP_ERR_NOT_OPEN | The control block has not been opened |
| FSP_ERR_ETHER_PHY_ERROR_LINK | PHY-LSI is not link up. |
| FSP_ERR_NOT_INITIALIZED | The control block has not been initialized |
| FSP_ERR_INVALID_MODE | Function is called when not in OPERATION mode. |
◆ R_RMAC_PHY_ChipInit()
Initialize Ethernet PHY device. Implements ether_phy_api_t::chipInit.
- Return values
-
| FSP_SUCCESS | PHY device initialized successfully. |
| FSP_ERR_ASSERTION | Pointer to RMAC_PHY control block or configuration structure is NULL. |
| FSP_ERR_NOT_OPEN | The control block has not been opened. |
| FSP_ERR_TIMEOUT | PHY-LSI Reset wait timeout. |
| FSP_ERR_INVALID_MODE | Function is called when not in OPERATION mode. |
◆ R_RMAC_PHY_Read()
Read data from register of PHY-LSI . Implements ether_phy_api_t::read.
- Return values
-
| FSP_SUCCESS | RMAC_PHY successfully read data. |
| FSP_ERR_ASSERTION | Pointer to RMAC_PHY control block is NULL. |
| FSP_ERR_INVALID_POINTER | Pointer to read buffer is NULL. |
| FSP_ERR_INVALID_ARGUMENT | Address is not a valid size |
| FSP_ERR_NOT_INITIALIZED | The control block has not been initialized |
| FSP_ERR_INVALID_MODE | Function is called when not in OPERATION mode. |
◆ R_RMAC_PHY_Write()
Write data to register of PHY-LSI . Implements ether_phy_api_t::write.
- Return values
-
| FSP_SUCCESS | RMAC_PHY successfully write data. |
| FSP_ERR_ASSERTION | Pointer to RMAC_PHY control block is NULL. |
| FSP_ERR_INVALID_ARGUMENT | Address or data is not a valid size |
| FSP_ERR_NOT_INITIALIZED | The control block has not been initialized |
| FSP_ERR_INVALID_MODE | Function is called when not in OPERATION mode. |
◆ R_RMAC_PHY_ChipSelect()
Update the target PHY LSI of this driver.
- Return values
-
| FSP_SUCCESS | PHY device initialized successfully. |
| FSP_ERR_ASSERTION | Pointer to RMAC_PHY control block or configuration structure is NULL. |
| FSP_ERR_NOT_OPEN | The control block has not been opened. |
| FSP_ERR_INVALID_ARGUMENT | Invalid PHY LSI is selected. |
◆ R_RMAC_PHY_CallbackSet()
Updates the user callback with the option to provide memory for the callback argument structure. Implements ether_api_t::callbackSet.
- Return values
-
| FSP_SUCCESS | Callback updated successfully. |
| FSP_ERR_ASSERTION | A required pointer is NULL. |
| FSP_ERR_NOT_OPEN | The control block has not been opened. |
| FSP_ERR_NO_CALLBACK_MEMORY | p_callback is non-secure and p_callback_memory is either secure or NULL. |


