 |
RZV Flexible Software Package Documentation
Release v3.1.0
|
|
 |
RZV Flexible Software Package Documentation
Release v3.1.0
|
|
Functions | |
| fsp_err_t | R_FSP_VersionGet (fsp_pack_version_t *const p_version) |
| void | Reset_Handler_NS (void) |
| void | Default_Handler (void) |
| void | NMI_Handler_NS (void) |
| void | Reset_Handler_S (void) |
| void | Default_Handler_S (void) |
| void | NMI_Handler_S (void) |
| void | SecureFault_Handler (void) |
| void | SystemInit (void) |
| void | R_BSP_WarmStart (bsp_warm_start_event_t event) |
| void | R_BSP_SecurityInit (void) |
| void | SystemInit_S (void) |
| __attribute__ ((naked)) | |
| uint32_t | R_FSP_SystemClockHzGet (fsp_priv_clock_t clock) |
| fsp_err_t | R_BSP_ClockSelectorSet (fsp_priv_clock_selector_t selector, uint32_t clock_sel) |
| fsp_err_t | R_BSP_ClockDividerSet (fsp_priv_clock_divider_t divider, uint32_t clock_div) |
| void | R_BSP_SoftwareDelay (uint32_t delay, bsp_delay_units_t units) |
| fsp_err_t | R_BSP_GroupIrqWrite (bsp_grp_irq_t irq, void(*p_callback)(bsp_grp_irq_t irq)) |
| __STATIC_INLINE IRQn_Type | R_FSP_CurrentIrqGet (void) |
| __STATIC_INLINE bsp_unique_id_t const * | R_BSP_UniqueIdGet () |
| void | R_BSP_IrqStatusClear (IRQn_Type irq) |
| void | R_BSP_IrqClearPending (IRQn_Type irq) |
| void | R_BSP_IrqCfg (IRQn_Type const irq, uint32_t priority, void *p_context) |
| void | R_BSP_IrqEnableNoClear (IRQn_Type const irq) |
| void | R_BSP_IrqEnable (IRQn_Type const irq) |
| void | R_BSP_IrqDisable (IRQn_Type const irq) |
| void | R_BSP_IrqCfgEnable (IRQn_Type const irq, uint32_t priority, void *p_context) |
| __STATIC_INLINE void | R_BSP_CacheCleanAllData (void) |
| __STATIC_INLINE void | R_BSP_CacheInvalidateAllData (void) |
| __STATIC_INLINE void | R_BSP_CacheInvalidateAllInst (void) |
| __STATIC_INLINE void | R_BSP_CacheCleanInvalidateAllData (void) |
| __STATIC_INLINE void | R_BSP_CacheCleanRangeData (void *addr, uint32_t length) |
| __STATIC_INLINE void | R_BSP_CacheInvalidateRangeData (void *addr, uint32_t length) |
| __STATIC_INLINE void | R_BSP_CacheInvalidateRangeInst (void *addr, uint32_t length) |
| __STATIC_INLINE void | R_BSP_CacheCleanInvalidateRangeData (void *addr, uint32_t length) |
| void | R_BSP_IrqDetectTypeSet (IRQn_Type const irq, uint8_t detect_type) |
| uint32_t | R_BSP_IrqPendingGet (IRQn_Type irq) |
| void | R_BSP_IrqGroupSet (IRQn_Type const irq, uint32_t interrupt_group) |
| void | R_BSP_IrqMaskLevelSet (uint32_t mask_level) |
| uint32_t | R_BSP_IrqMaskLevelGet (void) |
The BSP is responsible for getting the MPU from reset to the user's application. Before reaching the user's application, the BSP sets up the stacks, heap, clocks, interrupts, C runtime environment, and stack monitor.
The BSP and each driver operate according to the clock information output to bsp_clock_cfg.h. This clock information is provided from the Clocks tab of the configuration editor. The clock information is registered in a table inside the BSP when the BSP is initialized. The clock information is mainly used as follows.
Some BSP functions, such as exception handlers, can be replaced with user code if required. This is accomplished through the use of the 'weak' attribute. The weak attribute causes the declaration to be emitted as a weak symbol rather than a global. A weak symbol is one that can be overridden by an accompanying strong reference with the same name. When the BSP declares a function as weak, user code can define the same function and it will be used in place of the BSP function.
Weak symbols are supported for ELF targets and also for a.out targets when using the GNU assembler and linker.
Note that in CMSIS system.c, there is also a weak definition (and a function body) for the Warm Start callback function R_BSP_WarmStart(). Because this function is defined in the same file as the weak declaration, it will be called as the 'default' implementation. The function may be overridden by copying the body into their user application and modifying it as necessary. The linker identifies this as the 'strong' reference and uses it.
RZ MPU controls exceptions based on the ARM architecture. The BSP for each core provides exception handler functions to handle exceptions. Except for some exception handler functions, these functions are defined with the Weak attribute, so you can use the symbols of these functions to add your own exception handling code. By doing so, the user's exception handler function will be called instead of the exception handler function provided by the BSP.
Note that the exception handler functions provided by the BSP that are defined with the Weak attribute implement infinite loop processing to prevent runaways.
Exception information for each core is shown below.
Cortex-M core:
The Cortex-M core and NVIC (Nested Vectored Interrupt Controller) handle exceptions, interrupt configuration, prioritization, and interrupt masking. To handle exceptions, the core refers to a vector table where exception handler functions are registered. The Cortex-M vector table manages the table by exception number, and exception handlers are registered from 1 to 15. Exception number 0 is reserved for the MSP (Main Stack Pointer). In addition, peripheral interrupt handler functions are registered from exception number 16 onwards, and the corresponding function is called according to the number of the interrupt that occurred.
Below is a list of exception handler functions.
| Exception number | Exception Type | Exception Handler Symbol |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | MSP initialize | None |
| 1 | Reset | Reset_Handler_S (Note) |
| 2 | NMI | NMI_Handler_S (Note) |
| 3 | Hard Fault | HardFault_Handler_S |
| 4 | MPU Fault | MemManage_Handler_S |
| 5 | Bus Fault | BusFault_Handler_S |
| 6 | Usage Fault | UsageFault_Handler_S |
| 6 | Secure Fault | SecureFault_Handler (Note) |
| 7 - 10 | Reserved | None |
| 11 | SVCall | SVC_Handler_S |
| 12 | Debug Monitor | DebugMon_Handler_S |
| 13 | Reserved | None |
| 14 | PendSV | PendSV_Handler_S |
| 15 | SysTick | SysTick_Handler_S |
| 16 to (16 + N) | Peripheral Interrput 0 to N | Interrupt Handler Functions |
(Note) These functions cannot be changed.
Cortex-R core:
The Cortex-R core and the ARM Generic Interrupt Controller (GIC) handle exceptions, interrupt configuration, prioritization, and interrupt masking. To handle exceptions, the core references a vector table in which exception handler functions are registered. The Cortex-R vector table manages the table with an offset from the top address of the table, and exception handlers are registered at offsets 0x00 to 0x1F. The interrupt handler function is called by software control in the IRQ_handler.
The exception handler functions are listed below.
| Offset | Exception Type | Exception Handler Symbol |
|---|---|---|
| 0x00 | Reset | Reset_Handler (Note) |
| 0x04 | Undefined Instruction | Undefined_Handler |
| 0x08 | Supervisor Call | SVC_Handler |
| 0x0C | Prefetch Abort | Prefetch_Handler |
| 0x10 | Data Abort | Abort_Handler |
| 0x14 | Resorved | Reserved |
| 0x18 | IRQ interrupt | IRQ_Handler |
| 0x1C | FIQ interrupt | FIQ_Handler |
(Note) This function cannot be changed.
Group Interrupts are not supported in this device.
RZ MPU supports 480 peripheral interrupts by NVIC or GIC, and any factor can be registered in the vector table from the Interrupts tab of the Configuration editor.
Some MPUs have interrupts that can be assigned to multiple interrupt sources. These types of interrupts are called "Select Interrupts". When an interrupt that is the target of Select Interrupts is registered on the Smart Configurator, a number is automatically assigned. Therefore, the interrupt can be used without being aware of the changing interrupt number. However, there is a limit to the number of Select Interrupts that can be used depending on the core used by the FSP Project.
Below is a list of MPU that have Select Interrputs and the interrupt numbers to which the Select Interrupts are assigned.
| Core | Number of Select Interrupts | Assgined Interrupt No. |
|---|---|---|
| RZ/V2H Cortex-M33 | 127 | No.353 - 479 |
| RZ/V2H Cortex-R8 core0 | 85 | No.353 - 437 |
| RZ/V2H Cortex-R8 core1 | 42 | No.438 - 479 |
| RZ/V2N Cortex-M33 | 127 | No.353 - 479 |
As the BSP is in the process of bringing up the board out of reset, the callbacks are called at three points. These are defined as the 'Pre Clock Init', 'Post Clock Init' and 'Post C' warm start callbacks.
As described above, this function is already weakly defined as R_BSP_WarmStart(), so it is a simple matter of redefining the function or copying the existing body from CMSIS system.c into the application code to get a callback. R_BSP_WarmStart() takes an event parameter of type bsp_warm_start_event_t which describes the type of warm start callback being made.
This function is not enabled/disabled and is always called for both events as part of the BSP startup. Therefore it needs a function body, but it will not be called if it is overridden by a function symbol of the same name added within your application code. The function body is located in system.c. To use this function just copy this function into your own code and modify it to meet your needs.
In this BSP configuration, the FSP C runtime initialization code is skipped by setting "C Runtime Initialization" to "Disabled" on the BSP tab of the Configuration editor. Disabling this option is useful in cases where a non-standard linker script is being used or other modifications to the runtime initialization are desired. If this macro is disabled, your own run-time initialization code must be executed using the "Post Clock Init" event from a warm start (described above).
There is a limited amount of on-chip SRAM available, and some MPU have no memory protection, so heap usage must be very carefully controlled to avoid memory leaks, overruns, and attempts to over-allocate. Depending on the amount of memory your application requires, allocate a heap by setting a positive value for the "Heap size (bytes)" option in the Common configurations on the BSP tab.
When error logging is enabled, the error logging function can be redefined on the command line by defining FSP_ERROR_LOG(err) to the desired function call. The default function implementation is FSP_ERROR_LOG(err)=fsp_error_log(err, FILE, LINE). This implementation uses the predefined macros FILE and LINE to help identify the location where the error occurred. Removing the line from the function call can reduce code size when error logging is enabled. Some compilers may support other predefined macros like FUNCTION, which could be helpful for customizing the error logger.
This feature is not supported on this device.
This feature is not supported on this device.
Implements a blocking software delay. A delay can be specified in microseconds, milliseconds or seconds. The delay is implemented based on the system clock rate.
Implements a critical section. Some MPUs (MPUs with the BASEPRI register) support allowing high priority interrupts to execute during critical sections. On these MPUs, interrupts with priority less than or equal to BSP_CFG_IRQ_MASK_LEVEL_FOR_CRITICAL_SECTION are not serviced in critical sections. Interrupts with higher priority than BSP_CFG_IRQ_MASK_LEVEL_FOR_CRITICAL_SECTION still execute in critical sections.
This feature is not supported on this device.
The BSP will call the board's initialization function (bsp_init) which can initialize board specific features.
The BSP is heavily data driven with most features and functionality being configured based on the content from configuration files. Configuration files represent the settings on the Configuration editor and are generated when the project is built and/or when the Generate Project Content button is clicked in the Configuration editor.
Cortex-M core:
| Configuration | Options | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Secure stack size (bytes) | Value must be an integer multiple of 8 and between 8 and 0xFFFFFFFF | 0x200 | Set the size of the secure program stack. NOTE: This entry is for the secure stack. |
| Main stack size (bytes) | Value must be an integer multiple of 8 and between 8 and 0xFFFFFFFF | 0x200 | Set the size of the main program stack. NOTE: This entry is for the main stack. When using an RTOS, thread stacks can be configured in the properties for each thread. |
| Heap size (bytes) | Value must be 0 or an integer multiple of 8 between 8 and 0xFFFFFFFF. | 0 | The main heap is disabled by default. Set the heap size to a positive integer divisible by 8 to enable it. A minimum of 4K (0x1000) is recommended if standard library functions are to be used. |
| MCU Vcc (mV) | Value must between 0 and 5500 (5.5V) | 3300 | Some peripherals require different settings based on the supplied voltage. Entering Vcc here (in mV) allows the relevant driver modules to configure the associated peripherals accordingly. |
| Parameter checking |
| Disabled | When enabled, parameter checking for the BSP is turned on. In addition, any modules whose parameter checking configuration is set to 'Default (BSP)' will perform parameter checking as well. |
| Assert Failures |
| Return FSP_ERR_ASSERTION | Define the behavior of the FSP_ASSERT() macro. |
| Error Log |
| No Error Log | Specify error logging behavior. |
| PFS Protect |
| Enabled | Keep the PFS registers locked when they are not being modified. If disabled they will be unlocked during startup. |
| C Runtime Initialization |
| Enabled | Select if the C runtime initialization in the BSP is to be used. If disabled, use the BSP_WARM_START_POST_CLOCK event to run user defined equivalent. |
| Early BSP Initialization |
| Disabled | Enable this option to use BSP functions before C runtime initialization (BSP_WARM_START_RESET or BSP_WARM_START_POST_CLOCK). |
Cortex-R core:
The following build time configurations are defined in fsp_cfg/bsp/bsp_cfg.h:
| Configuration | Options | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| FIQ stack size | Value must be an integer multiple of 8 and between 8 and 0xFFFFFFFF | 0x1000 | Set the size of the FIQ mode program stack. |
| IRQ stack size | Value must be an integer multiple of 8 and between 8 and 0xFFFFFFFF | 0x1000 | Set the size of the IRQ mode program stack. |
| ABT stack size | Value must be an integer multiple of 8 and between 8 and 0xFFFFFFFF | 0x1000 | Set the size of the Abort mode program stack. |
| UND stack size | Value must be an integer multiple of 8 and between 8 and 0xFFFFFFFF | 0x1000 | Set the size of the Undefined mode program stack. |
| SYS stack size | Value must be an integer multiple of 8 and between 8 and 0xFFFFFFFF | 0x1000 | Set the size of the System mode program stack. |
| SVC stack size | Value must be an integer multiple of 8 and between 8 and 0xFFFFFFFF | 0x1000 | Set the size of the Supervisor mode program stack. |
| Heap size (bytes) | Value must be an integer multiple of 8 and between 8 and 0xFFFFFFFF | 0x1000 | Set the heap size to a positive integer divisible by 8 to enable it. A minimum of 4K (0x1000) is recommended if standard library functions are to be used. |
| MCU Vcc (mV) | Value must between 0 and 5500 (5.5V) | 3300 | Some peripherals require different settings based on the supplied voltage. Entering Vcc here (in mV) allows the relevant driver modules to configure the associated peripherals accordingly. |
| Parameter checking | - Disabled - Enabled | Disabled | When enabled, parameter checking for the BSP is turned on. In addition, any modules whose parameter checking configuration is set to 'Default (BSP)' will perform parameter checking as well. |
| Assert Failures | - Return FSP_ERR_ASSERTION - Call fsp_error_log then Return FSP_ERR_ASSERTION - Use assert() to Halt Execution - Disable checks that would return FSP_ERR_ASSERTION | Return FSP_ERR_ASSERTION | Define the behavior of the FSP_ASSERT() macro. |
| Error Log | - No Error Log - No Error Log | No Error Log | Specify error logging behavior. |
| PFS Protect | - Disabled - Enabled | Enabled | Keep the PFS registers locked when they are not being modified. If disabled they will be unlocked during startup. |
| C Runtime Initialization | - Disabled - Enabled | Enabled | Select if the C runtime initialization in the BSP is to be used. If disabled, use the BSP_WARM_START_POST_CLOCK event to run user defined equivalent. |
| Caches | - Disabled - Enabled | Enabled | Specifies whether to enable or disable the built-in cache. |
(Note) The following devices must signal a secure and privileged access protection signal when accessed:
Some cores have built-in cache. According to the BSP configuration, the cache is enabled after the clock information is registered in the table during the BSP initialization sequence. Enabling the cache will be available both the instruction cache and the data cache. For data cache, the memory space where the cache is enabled must be set as an attribute.
Below is a list of cores that have cache.
| Core | Cache |
|---|---|
| RZ/V2H Cortex-M33 | unsupported |
| RZ/V2H Cortex-R8 core0/core1 | supported |
| RZ/V2N Cortex-M33 | unsupported |
| RZ/V2L Cortex-M33 | unsupported |
Memory Attributes and can be set in the Memory Protection Unit (MPU, "MPU" refers to this unit in this chapter). The MPU is configured after anabling cache in the BSP initialization sequence. Below is a list of cores that have MPU.
| Core | MPU |
|---|---|
| RZ/V2H Cortex-M33 | unsupported |
| RZ/V2H Cortex-R8 core0/core1 | supported |
| RZ/V2N Cortex-M33 | unsupported |
| RZ/V2L Cortex-M33 | unsupported |
Configure it in the g_mpu_region_table_array[] table in the following file.
src/mpu_region_table.c
The structure of the table is shown below.
region number:
The MPU divides the memory space into several regions and sets Memory Attributes for each region. This parameter is the memory region number of the MPU for managing Memory Attribute setting.
On RZ/V2H Cortex-R8, region 0 to 15 are available.
base address:
Set the base address of the Memory Region. The address must be set to a value aligned with the size set in the size parameter.
Note the following when changing the address definition of a Memory Region.
The areas accessed by the program are assigned by the linker script. Therefore, if user modify the addresses of areas protected by the MPU in "src/mpu_region_table.c", user must also modify the addresses defined in linker script to match to it.
The linker script included in FSP defines the symbol settings for the MPU default settings as an example of the setting descriptions. The linker script symbols that correspond to the MPU default settings are listed in Default Memory Attribute for FSP below. Refer to this table when changing the MPU and linker script settings to suit your environment.
size:
Set the macro shown below to determine the size of the Memory Region. The address and size parameters must be set to cover the address range in which the memory is installed. If size is changed, the linker script should be modified for the same reason as the base address.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| BSP_MPU_SIZE_256B | region size = 256byte |
| BSP_MPU_SIZE_512B | region size = 512byte |
| BSP_MPU_SIZE_1KB | region size = 1Kbyte |
| BSP_MPU_SIZE_2KB | region size = 2Kbyte |
| BSP_MPU_SIZE_4KB | region size = 4Kbyte |
| BSP_MPU_SIZE_8KB | region size = 8Kbyte |
| BSP_MPU_SIZE_16KB | region size = 16Kbyte |
| BSP_MPU_SIZE_32KB | region size = 32Kbyte |
| BSP_MPU_SIZE_64KB | region size = 64Kbyte |
| BSP_MPU_SIZE_128KB | region size = 128Kbyte |
| BSP_MPU_SIZE_256KB | region size = 256Kbyte |
| BSP_MPU_SIZE_512KB | region size = 512Kbyte |
| BSP_MPU_SIZE_1MB | region size = 1Mbyte |
| BSP_MPU_SIZE_2MB | region size = 2Mbyte |
| BSP_MPU_SIZE_4MB | region size = 4Mbyte |
| BSP_MPU_SIZE_8MB | region size = 8Mbyte |
| BSP_MPU_SIZE_16MB | region size = 16Mbyte |
| BSP_MPU_SIZE_32MB | region size = 32Mbyte |
| BSP_MPU_SIZE_64MB | region size = 64Mbyte |
| BSP_MPU_SIZE_128MB | region size = 128Mbyte |
| BSP_MPU_SIZE_256MB | region size = 256Mbyte |
| BSP_MPU_SIZE_512MB | region size = 512Mbyte |
| BSP_MPU_SIZE_1GB | region size = 1Gbyte |
| BSP_MPU_SIZE_2GB | region size = 2Gbyte |
| BSP_MPU_SIZE_4GB | region size = 4Gbyte |
sub region enable:
Each Memory Region is divided into eight Sub regions, and Sub region 0 is the beginning of the Memory Region and Sub region 7 is the end of the Memory Region. You can disable MPU settings for each Sub region. For the area setting of a Sub region set to disable, the Memory Attribute settings of the lower priority region mapped there will be valid.
Configure it by setting the macro shown below to Sub region parameter.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| BSP_MPU_SUB_REGION_ALL_ENABLE | Enable all Sub regions. This macro cannot be used in combination with the Sub region disable macros. |
| BSP_MPU_SUB_REGION0_DISABLE | Disable Sub region 0. (Note) |
| BSP_MPU_SUB_REGION1_DISABLE | Disable Sub region 1. (Note) |
| BSP_MPU_SUB_REGION2_DISABLE | Disable Sub region 2. (Note) |
| BSP_MPU_SUB_REGION3_DISABLE | Disable Sub region 3. (Note) |
| BSP_MPU_SUB_REGION4_DISABLE | Disable Sub region 4. (Note) |
| BSP_MPU_SUB_REGION5_DISABLE | Disable Sub region 5. (Note) |
| BSP_MPU_SUB_REGION6_DISABLE | Disable Sub region 6. (Note) |
| BSP_MPU_SUB_REGION7_DISABLE | Disable Sub region 7. (Note) |
(Note) You can disable multiple Sub regions by combining macros that disable each Sub region.
To combine macros, write them as follows:
attribute:
Sets the Memory Region's Attributes. This value is set using a combination of Access Permission macro and Memory Attribute macro and Other macro.
Permission macro
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| BSP_MPU_ATTR_AP_PRIVILEGED_NOACCESS_USER_NOACCESS | Privileged mode: not accessible, user mode: not accessible |
| BSP_MPU_ATTR_AP_PRIVILEGED_READWRITE_USER_NOACCESS | Privileged mode: read/write possible, user mode: not accessible |
| BSP_MPU_ATTR_AP_PRIVILEGED_READWRITE_USER_READONLY | Privileged mode: read/write possible, user mode: read only |
| BSP_MPU_ATTR_AP_PRIVILEGED_READWRITE_USER_READWRITE | Privileged mode: read/write possible, user mode: read/write possible |
| BSP_MPU_ATTR_AP_PRIVILEGED_READONLY_USER_NOACCESS | Privileged mode: read only, user mode: not accessible |
| BSP_MPU_ATTR_AP_PRIVILEGED_READONLY_USER_READONLY | Privileged mode: readonly , user mode: read ony |
Memory Attribute macro
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| BSP_MPU_ATTR_TEX_C_B_STRONGLY_ORDERED | Memory Attribute: Strongly-Ordered memory |
| BSP_MPU_ATTR_TEX_C_B_DEVICE_SHAREABLE | Memory Attribute: Device memory, Shared |
| BSP_MPU_ATTR_TEX_C_B_DEVICE_NON_SHAREABLE | Memory Attribute: Device memory, Non-Shared |
| BSP_MPU_ATTR_TEX_C_B_NORMAL_OUTER_DISABLE_INNER_DISABLE | Memory Attribute: Normal memory, Outer Non-Cacheable, Inner Non-Cacheable |
| BSP_MPU_ATTR_TEX_C_B_NORMAL_OUTER_DISABLE_INNER_ENABLE | Memory Attribute: Normal memory, Outer Non-Cacheable, Inner Cacheable |
| BSP_MPU_ATTR_TEX_C_B_NORMAL_OUTER_ENABLE_INNER_DISABLE | Memory Attribute: Normal memory, Outer Cacheable, Inner Non-Cacheable |
| BSP_MPU_ATTR_TEX_C_B_NORMAL_OUTER_ENABLE_INNER_ENABLE | Memory Attribute: Normal memory, Outer Cacheable, Inner Cacheable |
Other Attribute macro
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| BSP_MPU_ATTR_XN | If this macro is set, programs will be prohibited from running in the region. If this macro is not set, programs will be allowed to run in the region. |
| BSP_MPU_ATTR_S | This is a macro to set Shared Normal memory. If this macro is not set, Non-shared Normal memory will be used. This macro can only be combined if the Normal memory attribute is set. Do not combine with Device memory or Strongly Ordered memory settings. |
An example of a setting using a combination of attribute macros is shown below.
This is an example of setting Shared Normal memory, program execution prohibited, and Read/Rrite permission in Privileged mode and User mode.
Example of attribute setting by region overlaping:
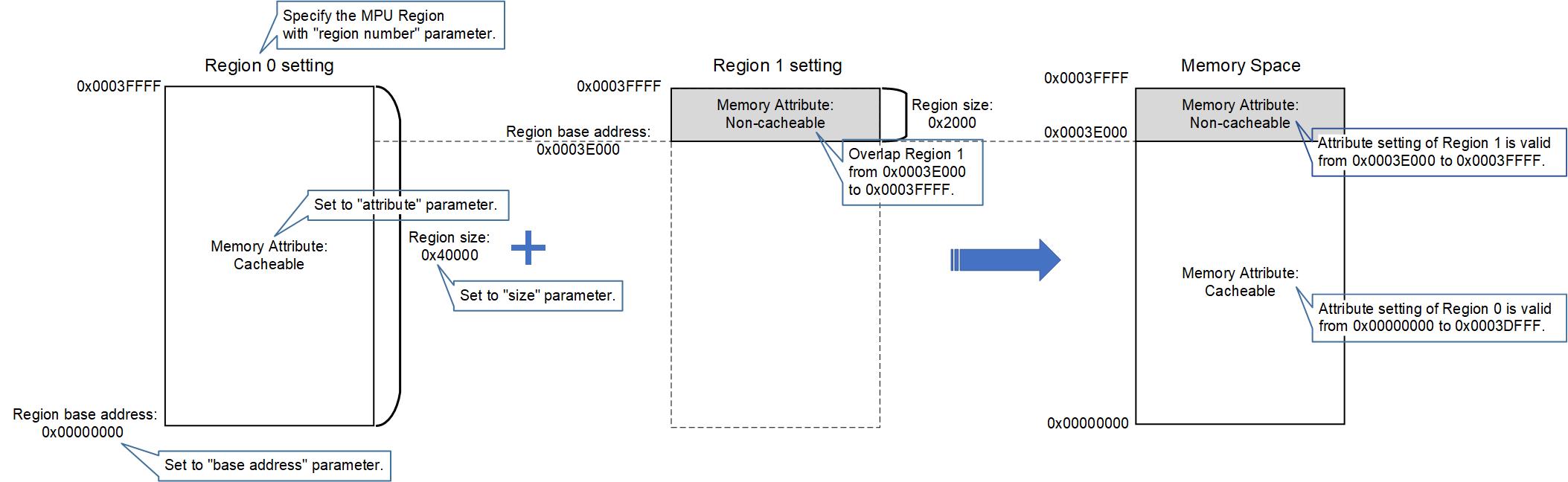
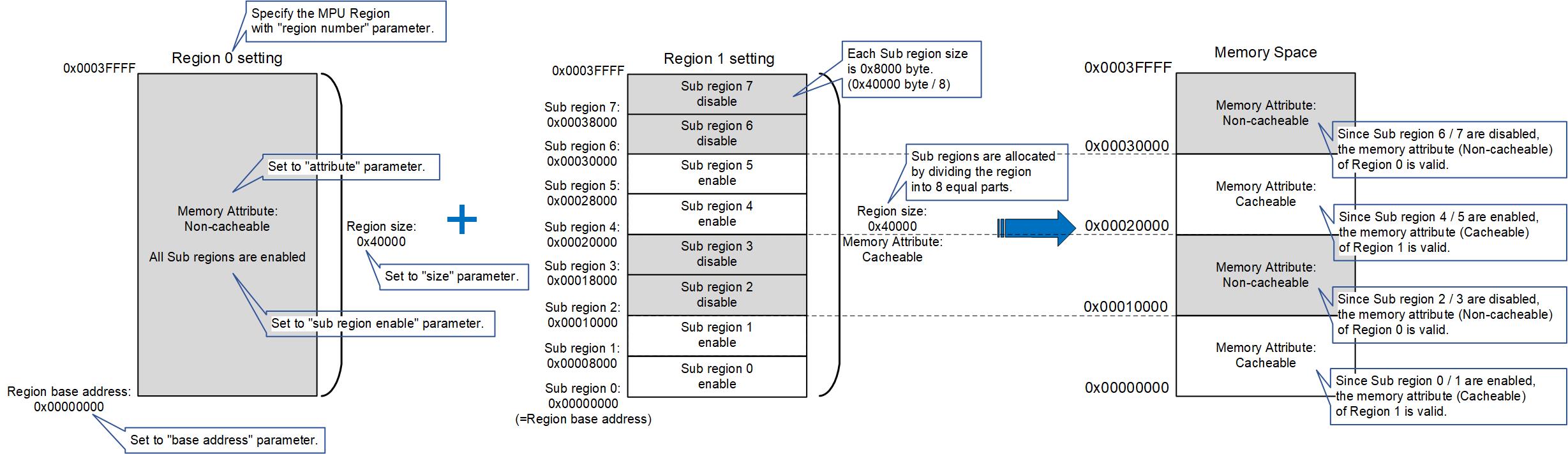
In the MPU, multiple regions can be set to the same address. When multiple regions overlap, the Memory Attributes of the region with the highest priority are set in the memory space. The priority depends on the region number, with larger numbers indicating higher priorities. This feature can be used to realize complex memory space layout.
The following Pattern 1 and Pattern 2 show examples of settings for complex memory space layout.
Pattern 1: Example of dividing one memory space into two memory spaces of different sizes.
Pattern 2: Example of setting four memory space layouts with two memory regions.
This example configuration uses the disable feature of the Sub region. When a Sub region is disabled, the memory space will have the attributes of the next highest priority region.
Default Memory Attribute for FSP:
The following list is the default Memory Attribute settings for FSP. This Memory Attribute is set in mpu_region_table.c.
for Cortex-R8 core0
| Region Number | Address | Memory Space Name | Attribute | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0x00000000 - 0x0001FFFF | ITCM | Normal Memory, Non-Shareable, Read/Write Enable, Execute Enable, Outer/Inner Non-cacheable | |
| 1 | 0x00020000 - 0x0003FFFF | DTCM | Normal Memory, Non-Shareable, Read/Write Enable, Execute Enable, Outer/Inner Non-cacheable | |
| 2 | 0x08100000 - 0x0819FFFF | RCPU SRAM (Cacheable) | Normal Memory, Non-Shareable, Read/Write Enable, Execute Enable, Outer Non-cacheable, Inner Cacheable | If the base address or size of this region is changed, the values of the symbols in the linker script shown below should be modified. SRAM_CACHE_PRV_START: base address SRAM_CACHE_PRV_LENGTH: size |
| 3 | 0x081A0000 - 0x081BFFFF | RCPU SRAM (Non-Cacheable) | Normal Memory, Non-Shareable, Read/Write Enable, Execute Enable, Outer/Inner Non-cacheable | If the base address or size of this region is changed, the values of the symbols in the linker script shown below should be modified. SRAM_UNCACHE_PRV_START: base address SRAM_UNCACHE_PRV_LENGTH: Set to the new value of size |
| 4 | 0x10000000 - 0x1FFFFFFF | Peripheral I/O | Device Memory, Non-Shareable, Read/Write Enable, Execute Disable, Outer/Inner Non-cacheable | |
| 5 | 0x20000000 - 0x2FFFFFFF | xSPI memory | Normal Memory, Non-Shareable, Read Enable, Execute Enable, Outer Non-cacheable, Inner Cacheable | If the base address or size of this region is changed, the values of the symbols in the linker script shown below should be modified. XSPIFLASH_PRV_START: base address XSPIFLASH_PRV_LENGTH: size |
| 6 | 0x40800000 - 0x40FFFFFF | DDR (Cacheable) | Normal Memory, Non-Shareable, Read/Write Enable, Execute Enable, Outer Non-cacheable, Inner Cacheable | If the base address or size of this region is changed, the values of the symbols in the linker script shown below should be modified. DDR_CACHE_PRV_START: base address DDR_CACHE_LENGTH: size |
| 7 | 0x41000000 - 0x417FFFFF | DDR (Non-cache) | Normal Memory, Non-Shareable, Read/Write Enable, Execute Enable, Outer/Inner Non-cacheable | If the base address or size of this region is changed, the values of the symbols in the linker script shown below should be modified. DDR_UNCACHE_PRV_START: base address DDR_UNCACHE_LENGTH: size |
| 8 | 0x42F00000 - 0x42F01FFF | OpenAMP RSCTBL + MHU SHMEM | Normal Memory, Shareable, Read/Write Enable, Execute Enable, Outer/Inner Non-cacheable | If the base address or size of this region is changed, the values of the symbols in the linker script shown below should be modified. OPENAMP_RSCTBL_START, MHU_SHMEM_START: base address OPENAMP_RSCTBL_LENGTH, MHU_SHMEM_LENGTH: size |
| 9 | 0x43000000 - 0x43FFFFFF | OpenAMP VRING | Normal Memory, Shareable, Read/Write Enable, Execute Enable, Outer/Inner Non-cacheable | If the base address or size of this region is changed, the values of the symbols in the linker script shown below should be modified. OPENAMP_VRING_START: base address OPENAMP_VRING_LENGTH: size |
| 10 to 15 | — | — | — | Unused region. If you want to add a region, add the corresponding area symbol to the linker script. |
for Cortex-R8 core1
| Region Number | Address | Memory Space Name | Attribute | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0x00000000 - 0x0001FFFF | ITCM | Normal Memory, Non-Shareable, Read/Write Enable, Execute Enable, Outer/Inner Non-cacheable | |
| 1 | 0x00020000 - 0x0003FFFF | DTCM | Normal Memory, Non-Shareable, Read/Write Enable, Execute Enable, Outer/Inner Non-cacheable | |
| 2 | 0x081C0000 - 0x081DFFFF | RCPU SRAM (Cacheable) | Normal Memory, Non-Shareable, Read/Write Enable, Execute Enable, Outer Non-cacheable, Inner Cacheable | If the base address or size of this region is changed, the values of the symbols in the linker script shown below should be modified. SRAM_CACHE_PRV_START: base address SRAM_CACHE_PRV_LENGTH: size |
| 3 | 0x081E0000 - 0x081FFFFF | RCPU SRAM (Non-Cacheable) | Normal Memory, Non-Shareable, Read/Write Enable, Execute Enable, Outer/Inner Non-cacheable | If the base address or size of this region is changed, the values of the symbols in the linker script shown below should be modified. SRAM_UNCACHE_PRV_START: base address SRAM_UNCACHE_PRV_LENGTH: size |
| 4 | 0x10000000 - 0x1FFFFFFF | Peripheral I/O | Device Memory, Non-Shareable, Read/Write Enable, Execute Disable, Outer/Inner Non-cacheable | |
| 5 | 0x20000000 - 0x2FFFFFFF | xSPI memory | Normal Memory, Non-Shareable, Read Enable, Execute Enable, Outer Non-cacheable, Inner Cacheable | If the base address or size of this region is changed, the values of the symbols in the linker script shown below should be modified. XSPIFLASH_PRV_START: base address XSPIFLASH_PRV_LENGTH: size |
| 6 | 0x41800000 - 0x41FFFFFF | DDR (Cacheable) | Normal Memory, Non-Shareable, Read/Write Enable, Execute Enable, Outer Non-cacheable, Inner Cacheable | If the base address or size of this region is changed, the values of the symbols in the linker script shown below should be modified. DDR_CACHE_PRV_START: base address DDR_CACHE_LENGTH: size |
| 7 | 0x42000000 - 0x427FFFFF | DDR (Non-cache) | Normal Memory, Non-Shareable, Read/Write Enable, Execute Enable, Outer/Inner Non-cacheable | If the base address or size of this region is changed, the values of the symbols in the linker script shown below should be modified. DDR_UNCACHE_PRV_START: base address DDR_UNCACHE_LENGTH: size |
| 8 | 0x42F00000 - 0x42F01FFF | OpenAMP RSCTBL + MHU SHMEM | Normal Memory, Shareable, Read/Write Enable, Execute Enable, Outer/Inner Non-cacheable | If the base address or size of this region is changed, the values of the symbols in the linker script shown below should be modified. OPENAMP_RSCTBL_START, MHU_SHMEM_START: base address OPENAMP_RSCTBL_LENGTH, MHU_SHMEM_LENGTH: size |
| 9 | 0x43000000 - 0x43FFFFFF | OpenAMP VRING | Normal Memory, Shareable, Read/Write Enable, Execute Enable, Outer/Inner Non-cacheable | If the base address or size of this region is changed, the values of the symbols in the linker script shown below should be modified. OPENAMP_VRING_START: base address OPENAMP_VRING_LENGTH: size |
| 10 to 15 | — | — | — | Unused region. If you want to add a region, add the corresponding area symbol to the linker script. |
The linker script to be modified when changing the address of the protected area of each region of the MPU is included in the script folder.
Modules | |
| RZV2H | |
| RZV2L | |
| RZV2N | |
Enumerations | |
| enum | fsp_ip_t |
| enum | bsp_delay_units_t |
| enum | bsp_grp_irq_t |
| enum | bsp_warm_start_event_t |
| enum | bsp_warm_start_event_t |
Variables | |
| uint32_t SystemCoreClock | BSP_SECTION_EARLY_INIT |
| uint32_t SystemCoreClock | BSP_SECTION_EARLY_INIT |
| #define R_BSP_MODULE_START | ( | ip, | |
| ch | |||
| ) |
Cancels the module stop state.
| ip | fsp_ip_t enum value for the module to be started |
| ch | The channel. Use channel 0 for modules without channels. |
| #define R_BSP_MODULE_STOP | ( | ip, | |
| ch | |||
| ) |
Enables the module stop state.
| ip | fsp_ip_t enum value for the module to be stopped |
| ch | The channel. Use channel 0 for modules without channels. |
| #define R_BSP_MODULE_START_FSP_IP_GTM | ( | ip, | |
| ch | |||
| ) |
Cancel the module stop state.
| ip | fsp_ip_t enum value for the module to be stopped |
| ch | The channel. Use channel 0 for modules without channels. |
| #define R_BSP_MODULE_STOP_FSP_IP_GTM | ( | ip, | |
| ch | |||
| ) |
Enables the module stop state.
| ip | fsp_ip_t enum value for the module to be stopped |
| ch | The channel. Use channel 0 for modules without channels. |
| #define R_BSP_MODULE_START_FSP_IP_GPT | ( | ip, | |
| ch | |||
| ) |
Cancel the module stop state.
| ip | fsp_ip_t enum value for the module to be stopped |
| ch | The channel. Use channel 0 for modules without channels. |
| #define R_BSP_MODULE_STOP_FSP_IP_GPT | ( | ip, | |
| ch | |||
| ) |
Enables the module stop state.
| ip | fsp_ip_t enum value for the module to be stopped |
| ch | The channel. Use channel 0 for modules without channels. |
| #define R_BSP_MODULE_START_FSP_IP_CANFD | ( | ip, | |
| ch | |||
| ) |
Cancel the module stop state.
| ip | fsp_ip_t enum value for the module to be stopped |
| ch | The channel. Use channel 0 for modules without channels. |
| #define R_BSP_MODULE_STOP_FSP_IP_CANFD | ( | ip, | |
| ch | |||
| ) |
Enables the module stop state.
| ip | fsp_ip_t enum value for the module to be stopped |
| ch | The channel. Use channel 0 for modules without channels. |
| #define R_BSP_MODULE_START_FSP_IP_ADC | ( | ip, | |
| ch | |||
| ) |
Cancel the module stop state.
| ip | fsp_ip_t enum value for the module to be stopped |
| ch | The channel. Use channel 0 for modules without channels. |
| #define R_BSP_MODULE_STOP_FSP_IP_ADC | ( | ip, | |
| ch | |||
| ) |
Enables the module stop state.
| ip | fsp_ip_t enum value for the module to be stopped |
| ch | The channel. Use channel 0 for modules without channels. |
| #define R_BSP_MODULE_START_FSP_IP_MHU | ( | ip, | |
| ch | |||
| ) |
Cancel the module stop state.
| ip | fsp_ip_t enum value for the module to be stopped |
| ch | The channel. Use channel 0 for modules without channels. |
| #define R_BSP_MODULE_STOP_FSP_IP_MHU | ( | ip, | |
| ch | |||
| ) |
Enables the module stop state.
| ip | fsp_ip_t enum value for the module to be stopped |
| ch | The channel. Use channel 0 for modules without channels. |
| #define R_BSP_MODULE_START_FSP_IP_POEG | ( | ip, | |
| ch | |||
| ) |
Cancel the module stop state.
| ip | fsp_ip_t enum value for the module to be stopped |
| ch | The channel. Use channel 0 for modules without channels. |
| #define R_BSP_MODULE_STOP_FSP_IP_POEG | ( | ip, | |
| ch | |||
| ) |
Enables the module stop state.
| ip | fsp_ip_t enum value for the module to be stopped |
| ch | The channel. Use channel 0 for modules without channels. |
| #define R_BSP_MODULE_START_FSP_IP_RIIC | ( | ip, | |
| ch | |||
| ) |
Cancel the module stop state.
| ip | fsp_ip_t enum value for the module to be stopped |
| ch | The channel. Use channel 0 for modules without channels. |
| #define R_BSP_MODULE_STOP_FSP_IP_RIIC | ( | ip, | |
| ch | |||
| ) |
Enables the module stop state.
| ip | fsp_ip_t enum value for the module to be stopped |
| ch | The channel. Use channel 0 for modules without channels. |
| #define R_BSP_MODULE_START_FSP_IP_SCI | ( | ip, | |
| ch | |||
| ) |
Cancel the module stop state.
| ip | fsp_ip_t enum value for the module to be stopped |
| ch | The channel. Use channel 0 for modules without channels. |
| #define R_BSP_MODULE_STOP_FSP_IP_SCI | ( | ip, | |
| ch | |||
| ) |
Enables the module stop state.
| ip | fsp_ip_t enum value for the module to be stopped |
| ch | The channel. Use channel 0 for modules without channels. |
| #define R_BSP_MODULE_START_FSP_IP_RSPI | ( | ip, | |
| ch | |||
| ) |
Cancel the module stop state.
| ip | fsp_ip_t enum value for the module to be stopped |
| ch | The channel. Use channel 0 for modules without channels. |
| #define R_BSP_MODULE_STOP_FSP_IP_RSPI | ( | ip, | |
| ch | |||
| ) |
Enables the module stop state.
| ip | fsp_ip_t enum value for the module to be stopped |
| ch | The channel. Use channel 0 for modules without channels. |
| #define R_BSP_MODULE_START_FSP_IP_TSU | ( | ip, | |
| ch | |||
| ) |
Cancel the module stop state.
| ip | fsp_ip_t enum value for the module to be stopped |
| ch | The channel. Use channel 0 for modules without channels. |
| #define R_BSP_MODULE_STOP_FSP_IP_TSU | ( | ip, | |
| ch | |||
| ) |
Enables the module stop state.
| ip | fsp_ip_t enum value for the module to be stopped |
| ch | The channel. Use channel 0 for modules without channels. |
| #define R_BSP_MODULE_START_FSP_IP_SCIF | ( | ip, | |
| ch | |||
| ) |
Cancel the module stop state.
| ip | fsp_ip_t enum value for the module to be stopped |
| ch | The channel. Use channel 0 for modules without channels. |
| #define R_BSP_MODULE_STOP_FSP_IP_SCIF | ( | ip, | |
| ch | |||
| ) |
Enables the module stop state.
| ip | fsp_ip_t enum value for the module to be stopped |
| ch | The channel. Use channel 0 for modules without channels. |
| #define R_BSP_MODULE_START_FSP_IP_DMAC | ( | ip, | |
| ch | |||
| ) |
Cancel the module stop state.
| ip | fsp_ip_t enum value for the module to be stopped |
| ch | The channel. Use channel 0 for modules without channels. |
| #define R_BSP_MODULE_STOP_FSP_IP_DMAC | ( | ip, | |
| ch | |||
| ) |
Enables the module stop state.
| ip | fsp_ip_t enum value for the module to be stopped |
| ch | The channel. Use channel 0 for modules without channels. |
| #define R_BSP_MODULE_START_FSP_IP_WDT | ( | ip, | |
| ch | |||
| ) |
Cancel the module stop state.
| ip | fsp_ip_t enum value for the module to be stopped |
| ch | The channel. Use channel 0 for modules without channels. |
| #define R_BSP_MODULE_STOP_FSP_IP_WDT | ( | ip, | |
| ch | |||
| ) |
Enables the module stop state.
| ip | fsp_ip_t enum value for the module to be stopped |
| ch | The channel. Use channel 0 for modules without channels. |
| #define R_BSP_MODULE_START_FSP_IP_MTU3 | ( | ip, | |
| ch | |||
| ) |
Cancel the module stop state.
| ip | fsp_ip_t enum value for the module to be stopped |
| ch | The channel. Use channel 0 for modules without channels. |
| #define R_BSP_MODULE_STOP_FSP_IP_MTU3 | ( | ip, | |
| ch | |||
| ) |
Enables the module stop state.
| ip | fsp_ip_t enum value for the module to be stopped |
| ch | The channel. Use channel 0 for modules without channels. |
| #define R_BSP_MSTP_START | ( | ip, | |
| channel | |||
| ) |
Cancels the module stop state.
| ip | fsp_ip_t enum value for the module to be started. |
| channel | The channel. Use ch 0 for modules without channels. |
| #define R_BSP_MSTP_STOP | ( | ip, | |
| channel | |||
| ) |
Enables the module stop state.
| ip | fsp_ip_t enum value for the module to be stopped. |
| channel | The channel. Use ch 0 for modules without channels. |
| #define BSP_IRQ_DISABLED |
Used to signify that an interrupt factor is not available.
| #define FSP_LOG_PRINT | ( | X | ) |
Macro that can be defined in order to enable logging in FSP modules.
| #define FSP_RETURN | ( | err | ) |
Macro to log and return error without an assertion.
| #define FSP_ERROR_LOG | ( | err | ) |
This function is called before returning an error code. To stop on a runtime error, define fsp_error_log in user code and do required debugging (breakpoints, stack dump, etc) in this function.
| #define FSP_ASSERT | ( | a | ) |
Default assertion calls FSP_ERROR_RETURN if condition "a" is false. Used to identify incorrect use of API's in FSP functions.
| #define FSP_ERROR_RETURN | ( | a, | |
| err | |||
| ) |
All FSP error codes are returned using this macro. Calls FSP_ERROR_LOG function if condition "a" is false. Used to identify runtime errors in FSP functions.
| #define FSP_CRITICAL_SECTION_ENTER |
This macro temporarily saves the current interrupt state and disables interrupts.
| #define FSP_CRITICAL_SECTION_EXIT |
This macro restores the previously saved interrupt state, reenabling interrupts.
| #define FSP_INVALID_VECTOR |
Used to signify that the requested IRQ vector is not defined in this system.
| #define BSP_CFG_HANDLE_UNRECOVERABLE_ERROR | ( | x | ) |
In the event of an unrecoverable error the BSP will by default call the __BKPT() intrinsic function which will alert the user of the error. The user can override this default behavior by defining their own BSP_CFG_HANDLE_UNRECOVERABLE_ERROR macro.
| #define BSP_STACK_ALIGNMENT |
Stacks (and heap) must be sized and aligned to an integer multiple of this number.
| #define BSP_IRQ_DISABLED |
Used to signify that an interrupt factor is not available.
| #define FSP_LOG_PRINT | ( | X | ) |
Macro that can be defined in order to enable logging in FSP modules.
| #define FSP_RETURN | ( | err | ) |
Macro to log and return error without an assertion.
| #define FSP_ERROR_LOG | ( | err | ) |
This function is called before returning an error code. To stop on a runtime error, define fsp_error_log in user code and do required debugging (breakpoints, stack dump, etc) in this function.
| #define FSP_ASSERT | ( | a | ) |
Default assertion calls FSP_ERROR_RETURN if condition "a" is false. Used to identify incorrect use of API's in FSP functions.
| #define FSP_ERROR_RETURN | ( | a, | |
| err | |||
| ) |
All FSP error codes are returned using this macro. Calls FSP_ERROR_LOG function if condition "a" is false. Used to identify runtime errors in FSP functions.
| #define FSP_CRITICAL_SECTION_ENTER |
This macro temporarily saves the current interrupt state and disables interrupts.
| #define FSP_CRITICAL_SECTION_EXIT |
This macro restores the previously saved interrupt state, reenabling interrupts.
| #define FSP_INVALID_VECTOR |
Used to signify that the requested IRQ vector is not defined in this system.
| #define BSP_CFG_HANDLE_UNRECOVERABLE_ERROR | ( | x | ) |
In the event of an unrecoverable error the BSP will by default call the __BKPT() intrinsic function which will alert the user of the error. The user can override this default behavior by defining their own BSP_CFG_HANDLE_UNRECOVERABLE_ERROR macro.
| #define BSP_STACK_ALIGNMENT |
Stacks (and heap) must be sized and aligned to an integer multiple of this number.
| enum fsp_ip_t |
Available modules.
| enum bsp_delay_units_t |
Available delay units for R_BSP_SoftwareDelay(). These are ultimately used to calculate a total # of microseconds
| enum bsp_grp_irq_t |
Different warm start entry locations in the BSP.
Different warm start entry locations in the BSP.
| fsp_err_t R_FSP_VersionGet | ( | fsp_pack_version_t *const | p_version | ) |
Get the FSP version based on compile time macros.
| [out] | p_version | Memory address to return version information to. |
| FSP_SUCCESS | Version information stored. |
| FSP_ERR_ASSERTION | The parameter p_version is NULL. |
| void Reset_Handler_NS | ( | void | ) |
MPU starts executing here out of reset. Main stack pointer is set up already.
| void Default_Handler | ( | void | ) |
Default exception handler.
| void NMI_Handler_NS | ( | void | ) |
Non-maskable interrupt handler.
| void Reset_Handler_S | ( | void | ) |
MPU starts executing here out of reset. Main stack pointer is set up already.
| void Default_Handler_S | ( | void | ) |
Default exception handler.
| void NMI_Handler_S | ( | void | ) |
Non-maskable interrupt handler.
| void SecureFault_Handler | ( | void | ) |
SecureFault_Handler
| void SystemInit | ( | void | ) |
Initialize the MPU and the runtime environment.
| void R_BSP_WarmStart | ( | bsp_warm_start_event_t | event | ) |
This function is called at various points during the startup process. This function is declared as a weak symbol higher up in this file because it is meant to be overridden by a user implemented version. One of the main uses for this function is to call functional safety code during the startup process. To use this function just copy this function into your own code and modify it to meet your needs.
| [in] | event | Where the code currently is in the start up process |
| void R_BSP_SecurityInit | ( | void | ) |
Initialize security features for TrustZone.
This function initializes security register for secure projects.
| void SystemInit_S | ( | void | ) |
Initialize the MPU and the runtime environment.
| __attribute__ | ( | (naked) | ) |
In the Cortex-M33 CPU core of this device, the secure vector address must be set to SYS_CM33_CFG2 before WarmReset is executed. Also, the non-secure vector address must be set to SYS_CM33_CFG3 before WarmReset is executed. The Cortex-M33's program works on the assumption that the appropriate vector address values have been set in SYS_CM33_CFG2 and SYS_CM33_CFG3 in the Cortex-A55 program.
Entry function when debugging RAM load using a debugger
| uint32_t R_FSP_SystemClockHzGet | ( | fsp_priv_clock_t | clock | ) |
Get the system clock frequency.
| [in] | clock | Element number of the array that defines the frequency of the bus clock. |
| g_clock_freq[clock] | System clock frequency. |
| fsp_err_t R_BSP_ClockSelectorSet | ( | fsp_priv_clock_selector_t | selector, |
| uint32_t | clock_sel | ||
| ) |
Set a clock selector.
| [in] | selector | Element number of the array that defines the clock selector. |
| [in] | clock_sel | Value to set in Mux Control register. |
| FSP_SUCCESS | Selector configuration changes completed. |
| FSP_ERR_INVALID_ARGUMENT | Undefined selector specified. |
| FSP_ERR_PLL_SRC_INACTIVE | Clock source PLL is reset state. |
| fsp_err_t R_BSP_ClockDividerSet | ( | fsp_priv_clock_divider_t | divider, |
| uint32_t | clock_div | ||
| ) |
Set a clock division ratio.
| [in] | divider | Element number of the array that defines the clock divider. |
| [in] | clock_div | Value to set in Gear Control register. |
| FSP_SUCCESS | Divider configuration changes completed. |
| FSP_ERR_INVALID_ARGUMENT | Undefined divider specified. |
| FSP_ERR_PLL_SRC_INACTIVE | Clock source PLL is reset state. |
| void R_BSP_SoftwareDelay | ( | uint32_t | delay, |
| bsp_delay_units_t | units | ||
| ) |
Delay for at least the specified duration in units and return. This function shouldn't be used to generate an accurate delay time. A running time of the function is depending on the region of memory where the function is excuted on and a frequency of the CPU clock.
The loop time of bsp_prv_software_delay_loop() varies depending on the CPU clock frequency and the type of memory the program runs on. The loop time parameter is determined by measuring the actual execution time of bsp_prv_software_delay_loop(). The loop time parameter of software_delay_loop() can be changed by redefining the loop time parameter, BSP_FEATURE_BSP_DELAY_LOOP_CYCLES.
| [in] | delay | The number of 'units' to delay. |
| [in] | units | The 'base' (bsp_delay_units_t) for the units specified. Valid values are: BSP_DELAY_UNITS_SECONDS, BSP_DELAY_UNITS_MILLISECONDS, BSP_DELAY_UNITS_MICROSECONDS. For example: The case described is where one execution of bsp_prv_software_delay_loop() takes approximately 500ns, in which case a 100us delay requires 100000ns / 500ns -> 200 loops. |
The 'theoretical' maximum delay that may be obtained is determined by a full 32 bit loop count and the system clock rate. @200MHz: ((0xFFFFFFFF loops * 500ns) = 2147 seconds.
Note that requests for very large delays will be affected by rounding in the calculations and the actual delay achieved may be slightly off of a setting time.
Note also that if the calculations result in a loop_cnt of zero, the bsp_prv_software_delay_loop() function is not called at all. In this case the requested delay is too small (nanoseconds) to be carried out by the loop itself, and the overhead associated with executing the code to just get to this point has certainly satisfied the requested delay.
| fsp_err_t R_BSP_GroupIrqWrite | ( | bsp_grp_irq_t | irq, |
| void(*)(bsp_grp_irq_t irq) | p_callback | ||
| ) |
Register a callback function for supported interrupts. If NULL is passed for the callback argument then any previously registered callbacks are unregistered.
| [in] | irq | Interrupt for which to register a callback. |
| [in] | p_callback | Pointer to function to call when interrupt occurs. |
| FSP_ERR_UNSUPPORTED | NMI Group IRQ are not supported in this device. |
| __STATIC_INLINE IRQn_Type R_FSP_CurrentIrqGet | ( | void | ) |
Return active interrupt vector number value
| __STATIC_INLINE bsp_unique_id_t const * R_BSP_UniqueIdGet | ( | ) |
Get unique ID is not supported in this device.
| void R_BSP_IrqStatusClear | ( | IRQn_Type | irq | ) |
Clear the interrupt status flag for a given interrupt.
| [in] | irq | Not used |
| void R_BSP_IrqClearPending | ( | IRQn_Type | irq | ) |
Clear the interrupt status flag for a given interrupt and clear the NVIC pending interrupt.
| [in] | irq | Interrupt for which to clear the status flag. Note that the enums listed for IRQn_Type are only those for the Cortex Processor Exceptions Numbers. |
Clear the GIC pending interrupt.
| [in] | irq | Interrupt for which to clear the Pending bit. Note that the enums listed for IRQn_Type are only those for the Cortex Processor Exceptions Numbers. |
| void R_BSP_IrqCfg | ( | IRQn_Type const | irq, |
| uint32_t | priority, | ||
| void * | p_context | ||
| ) |
Sets the interrupt priority and context.
| [in] | irq | The IRQ to configure. |
| [in] | priority | NVIC priority of the interrupt |
| [in] | p_context | The interrupt context is a pointer to data required in the ISR. |
Sets the interrupt priority and context.
| [in] | irq | The IRQ number to configure. |
| [in] | priority | GIC priority of the interrupt |
| [in] | p_context | The interrupt context is a pointer to data required in the ISR. |
| void R_BSP_IrqEnableNoClear | ( | IRQn_Type const | irq | ) |
Enable the IRQ in the NVIC (Without clearing the pending bit).
| [in] | irq | The IRQ to enable. Note that the enums listed for IRQn_Type are only those for the Cortex Processor Exceptions Numbers. |
Enable the IRQ in the GIC (Without clearing the pending bit).
| [in] | irq | The IRQ number to enable. Note that the enums listed for IRQn_Type are only those for the Cortex Processor Exceptions Numbers. |
| void R_BSP_IrqEnable | ( | IRQn_Type const | irq | ) |
Clears pending interrupts in both IM33 and NVIC, then enables the interrupt.
| [in] | irq | Interrupt for which to clear status flag and enable in the NVIC. Note that the enums listed for IRQn_Type are only those for the Cortex Processor Exceptions Numbers. |
Enable the IRQ in the GIC (With clearing the pending bit).
| [in] | irq | The IRQ number to enable. Note that the enums listed for IRQn_Type are only those for the Cortex Processor Exceptions Numbers. |
| void R_BSP_IrqDisable | ( | IRQn_Type const | irq | ) |
Disables interrupts in the NVIC.
| [in] | irq | The IRQ to disable in the NVIC. Note that the enums listed for IRQn_Type are only those for the Cortex Processor Exceptions Numbers. |
Disables interrupts in the GIC.
| [in] | irq | The IRQ number to disable in the GIC. Note that the enums listed for IRQn_Type are only those for the Cortex Processor Exceptions Numbers. |
| void R_BSP_IrqCfgEnable | ( | IRQn_Type const | irq, |
| uint32_t | priority, | ||
| void * | p_context | ||
| ) |
Sets the interrupt priority and context, clears pending interrupts, then enables the interrupt.
| [in] | irq | Interrupt number. |
| [in] | priority | NVIC priority of the interrupt |
| [in] | p_context | The interrupt context is a pointer to data required in the ISR. |
Sets the interrupt priority and context, clears pending interrupts, then enables the interrupt.
| [in] | irq | Interrupt number. |
| [in] | priority | GIC priority of the interrupt |
| [in] | p_context | The interrupt context is a pointer to data required in the ISR. |
| __STATIC_INLINE void R_BSP_CacheCleanAllData | ( | void | ) |
Clean whole of the data cache.
| __STATIC_INLINE void R_BSP_CacheInvalidateAllData | ( | void | ) |
Invalidate whole of the data cache.
| __STATIC_INLINE void R_BSP_CacheInvalidateAllInst | ( | void | ) |
Invalidate whole of the instruction cache.
| __STATIC_INLINE void R_BSP_CacheCleanInvalidateAllData | ( | void | ) |
Clean and invalidate the whole of data cache.
| __STATIC_INLINE void R_BSP_CacheCleanRangeData | ( | void * | addr, |
| uint32_t | length | ||
| ) |
Clean the cache for the specified area.
| [in] | addr | Base address of area to clean. |
| [in] | length | Length of area to clean. |
| __STATIC_INLINE void R_BSP_CacheInvalidateRangeData | ( | void * | addr, |
| uint32_t | length | ||
| ) |
Invalidate the cache for the specified area.
| [in] | addr | Base address of area to invalidate. |
| [in] | length | Length of area to invalidate. |
| __STATIC_INLINE void R_BSP_CacheInvalidateRangeInst | ( | void * | addr, |
| uint32_t | length | ||
| ) |
Invalidate the instruction cache for the specified area.
| [in] | addr | Base address of area to invalidate. |
| [in] | length | Length of area to invalidate. |
| __STATIC_INLINE void R_BSP_CacheCleanInvalidateRangeData | ( | void * | addr, |
| uint32_t | length | ||
| ) |
Clean and invalidate the cache for the specified area.
| [in] | addr | Base address of area to clean and invalidate. |
| [in] | length | Length of area to clean and invalidate. |
| void R_BSP_IrqDetectTypeSet | ( | IRQn_Type const | irq, |
| uint8_t | detect_type | ||
| ) |
Sets the interrupt detect type.
| [in] | irq | The IRQ number to configure. |
| [in] | detect_type | GIC detect type of the interrupt (BSP_GIC_SPI_DETECT_LEVEL : level-sensitive, BSP_GIC_SPI_DETECT_EDGE : edge-triggerd). |
| uint32_t R_BSP_IrqPendingGet | ( | IRQn_Type | irq | ) |
Get the GIC pending interrupt.
| [in] | irq | Interrupt that gets a pending bit.. Note that the enums listed for IRQn_Type are only those for the Cortex Processor Exceptions Numbers. |
| void R_BSP_IrqGroupSet | ( | IRQn_Type const | irq, |
| uint32_t | interrupt_group | ||
| ) |
Sets the interrupt Group.
| [in] | irq | The IRQ number to configure. |
| [in] | interrupt_group | GIC interrupt group number ( 0 : FIQ, 1 : IRQ ). |
| void R_BSP_IrqMaskLevelSet | ( | uint32_t | mask_level | ) |
Sets the interrupt priority mask level.
| [in] | mask_level | The interrupt mask level |
| uint32_t R_BSP_IrqMaskLevelGet | ( | void | ) |
Gets the interruptpriority mask level.
| uint32_t SystemCoreClock BSP_SECTION_EARLY_INIT |
System Clock Frequency (Core Clock)
| uint32_t SystemCoreClock BSP_SECTION_EARLY_INIT |
System Clock Frequency (Core Clock)