 |
RZV Flexible Software Package Documentation
Release v3.1.0
|
|
 |
RZV Flexible Software Package Documentation
Release v3.1.0
|
|
Functions | |
| fsp_err_t | R_WDT_Refresh (wdt_ctrl_t *const p_ctrl) |
| fsp_err_t | R_WDT_Open (wdt_ctrl_t *const p_ctrl, wdt_cfg_t const *const p_cfg) |
| fsp_err_t | R_WDT_StatusClear (wdt_ctrl_t *const p_ctrl, const wdt_status_t status) |
| fsp_err_t | R_WDT_StatusGet (wdt_ctrl_t *const p_ctrl, wdt_status_t *const p_status) |
| fsp_err_t | R_WDT_CounterGet (wdt_ctrl_t *const p_ctrl, uint32_t *const p_count) |
| fsp_err_t | R_WDT_TimeoutGet (wdt_ctrl_t *const p_ctrl, wdt_timeout_values_t *const p_timeout) |
| fsp_err_t | R_WDT_CallbackSet (wdt_ctrl_t *const p_ctrl, void(*p_callback)(wdt_callback_args_t *), void const *const p_context, wdt_callback_args_t *const p_callback_memory) |
Driver for the WDT peripheral on RZ MPUs. This module implements the WDT Interface.
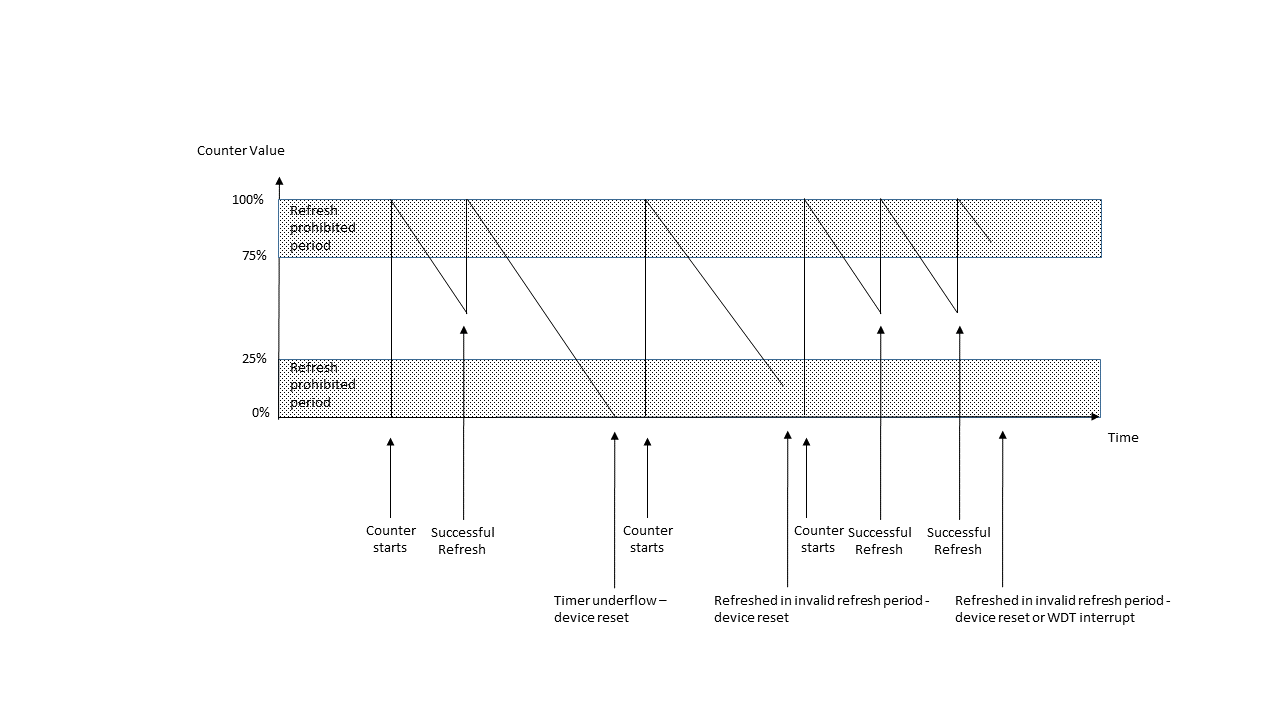
The watchdog timer is used to recover from unexpected errors in an application. The watchdog timer must be refreshed periodically in the permitted count window by the application. If the count is allowed to underflow or refresh occurs outside of the valid refresh period, the WDT resets the device or generates an IRQ.
The WDT HAL module has the following key features:
When using register start mode, configure the watchdog timer on the Stacks tab.
| Configuration | Options | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter Checking |
| Default (BSP) | If selected code for parameter checking is included in the build. |
| Configuration | Options | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Name must be a valid C symbol | g_wdt0 | Module name. |
| Channel | MCU Specific Options | Check User's Manual: Hardware to see which CPU a channel is for. | |
| Timeout | MCU Specific Options | Select the watchdog timeout in cycles. | |
| Clock Division Ratio | MCU Specific Options | Select the watchdog clock divisor. | |
| Window Start Position | MCU Specific Options | Select the allowed watchdog refresh start point in %. | |
| Window End Position | MCU Specific Options | Select the allowed watchdog refresh end point in %. | |
| WDT Counting | MCU Specific Options | Select to enable or disable WDT counting. It is recommended to set "WDT Counting" to "Disabled" to avoid unintentional WDT interrupt occurs when debugging the user program. | |
| System Reset | MCU Specific Options | Select to enable or disable system reset due to a request by WDT. | |
| WDTUDFOUT Assertion | MCU Specific Options | Select to enable or disable the assertion of WDTUDFOUT due to a request by WDT. | |
| Cold Reset | MCU Specific Options | Select to enable or disable the cold reset due to a request by WDT. | |
| Underflow Interrupt Enable | MCU Specific Options | Enable the WDT underflow interrupt. | |
| Underflow Interrupt Priority | Value must be an integer between 0 and 255 | 8 | Select the underflow interrupt priority. |
| WDT Callback | Name must be a valid C symbol | NULL | A user callback function must be provided if the WDT is configured to generate an NMI when the timer underflows or a refresh error occurs. If this callback function is provided, it will be called from the NMI handler each time the watchdog triggers. |
The WDT clock is based on the OSCCLK frequency. You can not set the OSCCLK frequency using the Clocks tab of the RZ Configuration editor or by using the CGC Interface at run-time. The maximum timeout period with OSCCLK running at 24 MHz is approximately 0.175 seconds.
This WDT uses the following pin.
The WDT operates from OSCCLK. With a OSCCLK of 24 MHz, the maximum time from the last refresh to device reset or IRQ generation will be just over 0.175 seconds as detailed below.
OSCCLK = 24 MHz
Clock division ratio = OSCCLK / 256
Timeout period = 16384 cycles
WDT clock frequency = 24 MHz / 256 = 93.750 kHz
Cycle time = 1 / 93.750 kHz = 10.667 us
Timeout = 10.667 us x 16384 cycles = 0.175 seconds
Developers should be aware of the following limitations when using the WDT:
WDT interrupt to CPU are prohibited in specific core.
| Device | Core | WDT interrupt to CPU |
|---|---|---|
| RZ/V2H | CM33 | Prohibited |
| CR8 | Not prohibited |
This is a basic example of minimal use of the WDT in an application.
This example demonstrates using a start window and gives an example callback to handle an IRQ generated by an underflow or refresh error.
Data Structures | |
| struct | wdt_instance_ctrl_t |
| struct | wdt_extended_cfg_t |
| struct wdt_instance_ctrl_t |
WDT private control block. DO NOT MODIFY. Initialization occurs when R_WDT_Open() is called.
| struct wdt_extended_cfg_t |
WDT configuration extension. This extension is required.
| fsp_err_t R_WDT_Refresh | ( | wdt_ctrl_t *const | p_ctrl | ) |
Refresh the watchdog timer. Implements wdt_api_t::refresh.
In addition to refreshing the watchdog counter this function can be used to start the counter in register start mode.
Example:
| FSP_SUCCESS | WDT successfully refreshed. |
| FSP_ERR_ASSERTION | p_ctrl is NULL. |
| FSP_ERR_NOT_OPEN | Instance control block is not initialized. |
| fsp_err_t R_WDT_Open | ( | wdt_ctrl_t *const | p_ctrl, |
| wdt_cfg_t const *const | p_cfg | ||
| ) |
Configures the WDT driver based on the input configurations. This function sets the callback function, the timeout count value, and enables the overflow interrupt. Implements wdt_api_t::open.
This function should only be called once as WDT configuration registers can only be written to once so subsequent calls will have no effect.
Example:
| FSP_SUCCESS | WDT successfully configured. |
| FSP_ERR_ASSERTION | Null pointer, or one or more configuration options is invalid. |
| FSP_ERR_ALREADY_OPEN | Module is already open. This module can only be opened once. |
| fsp_err_t R_WDT_StatusClear | ( | wdt_ctrl_t *const | p_ctrl, |
| const wdt_status_t | status | ||
| ) |
Clear the WDT status and error flags. Implements wdt_api_t::statusClear.
Example:
| FSP_SUCCESS | WDT flag(s) successfully cleared. |
| FSP_ERR_ASSERTION | Null pointer as a parameter. |
| FSP_ERR_NOT_OPEN | Instance control block is not initialized. |
| fsp_err_t R_WDT_StatusGet | ( | wdt_ctrl_t *const | p_ctrl, |
| wdt_status_t *const | p_status | ||
| ) |
Read the WDT status flags. Implements wdt_api_t::statusGet.
Indicates both status and error conditions.
Example:
| FSP_SUCCESS | WDT status successfully read. |
| FSP_ERR_ASSERTION | Null pointer as a parameter. |
| FSP_ERR_NOT_OPEN | Instance control block is not initialized. |
| fsp_err_t R_WDT_CounterGet | ( | wdt_ctrl_t *const | p_ctrl, |
| uint32_t *const | p_count | ||
| ) |
Read the current count value of the WDT. Implements wdt_api_t::counterGet.
Example:
| FSP_SUCCESS | WDT current count successfully read. |
| FSP_ERR_ASSERTION | Null pointer passed as a parameter. |
| FSP_ERR_NOT_OPEN | Instance control block is not initialized. |
| fsp_err_t R_WDT_TimeoutGet | ( | wdt_ctrl_t *const | p_ctrl, |
| wdt_timeout_values_t *const | p_timeout | ||
| ) |
Read timeout information for the watchdog timer. Implements wdt_api_t::timeoutGet.
| FSP_SUCCESS | WDT timeout information retrieved successfully. |
| FSP_ERR_ASSERTION | Null Pointer. |
| FSP_ERR_NOT_OPEN | Instance control block is not initialized. |
| fsp_err_t R_WDT_CallbackSet | ( | wdt_ctrl_t *const | p_ctrl, |
| void(*)(wdt_callback_args_t *) | p_callback, | ||
| void const *const | p_context, | ||
| wdt_callback_args_t *const | p_callback_memory | ||
| ) |
Updates the user callback and has option of providing memory for callback structure. Implements wdt_api_t::callbackSet
| FSP_SUCCESS | Callback updated successfully. |
| FSP_ERR_ASSERTION | A required pointer is NULL. |
| FSP_ERR_NOT_OPEN | The control block has not been opened. |
| FSP_ERR_NO_CALLBACK_MEMORY | p_callback is non-secure and p_callback_memory is either secure or NULL. |