 |
RZT Flexible Software Package Documentation
Release v3.1.0
|
|
 |
RZT Flexible Software Package Documentation
Release v3.1.0
|
|
Driver for the GPT peripherals on RZ microprocessor. This module implements the Timer Interface.
The GPT module can be used to count events, measure external input signals, generate a periodic interrupt, or output a periodic or PWM signal to a GTIOC pin.
This module supports the GPT peripherals are 32-bit timers. The 32-bit timers are all treated the same in this module from the API perspective.
The GPT module has the following features:
RZ microprocessor have timer peripherals: the General PWM Timer (GPT). When selecting between them, consider these factors:
| GPT | |
|---|---|
| Low Power Modes | The GPT can operate in sleep mode. |
| Available Channels | The number of GPT channels is device specific. All currently supported MCUs have at least 18 GPT channels. |
| Timer Resolution | All MCUs have at least one 32-bit GPT timer. |
| Clock Source | -Bus clock: PCLKH in LLPP, PCLKM in NONSAFETY, and PCLKM in SAFETY |
| -Core clock: PCLKGPT in LLPP, PCLKM in NONSAFETY, and PCLKM in SAFETY |
| Configuration | Options | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter Checking |
| Default (BSP) | If selected code for parameter checking is included in the build. |
| Pin Output Support |
| Disabled | Enables or disables support for outputting PWM waveforms on GTIOCx pins. The "Enabled with Extra Features" option enables support for Triangle wave modes and also enables the features located in the "Extra Features" section of each module instance. |
| Write Protect Enable |
| Disabled | If selected write protection is applied to all GPT channels. |
| Multiplex Interrupt |
| Disabled | Enable multiplex interrupt for a single driver. |
| Configuration | Options | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| General > Compare Match > Compare Match A > Status |
| Disabled | |
| General > Compare Match > Compare Match A > Compare match value | Value must be a non-negative integer less than or equal to 0x40000000000 | 0 | Specify the compare match A value in units that selected in Period Unit section. |
| General > Compare Match > Compare Match B > Status |
| Disabled | |
| General > Compare Match > Compare Match B > Compare match value | Value must be a non-negative integer less than or equal to 0x40000000000 | 0 | Specify the compare match B value in units that selected in Period Unit section. |
| General > Name | Name must be a valid C symbol | g_timer0 | Module name. |
| General > Unit | Unit number must exist on this MCU | 0 | Specify the hardware unit. For devices without units, each of the three groups(LLPP, NONSAFETY, and SAFETY) is treated as a unit. LLPP: Unit 0 NONSAFETY: Unit 1 SAFETY: Unit 2 |
| General > Channel | Channel number must exist on this MCU | 0 | Specify the hardware channel. For devices without units, set a different number than a hardware channel when using a channel in NONSAFETY or SAFETY group. |
| General > Mode |
| Periodic | Mode selection. Periodic: Generates periodic interrupts or square waves. One-shot: Generate a single interrupt or a pulse wave. Note: One-shot mode is implemented in software. ISRs must be enabled for one-shot even if callback is unused. One-Shot Pulse: Counter performs saw-wave operation with fixed buffer operation. Saw-wave PWM: Generates basic saw-wave PWM waveforms. Triangle-wave PWM (symmetric, Mode 1): Generates symmetric PWM waveforms with duty cycle determined by compare match set with 32-bit transfer during a crest event and updated at the next trough with single or double buffer operation. Triangle-wave PWM (asymmetric, Mode 2): Generates asymmetric PWM waveforms with duty cycle determined by compare match set with 32-bit transfer during a crest/trough event and updated at the next trough/crest. Triangle-wave PWM (asymmetric, Mode 3): Generates PWM waveforms with duty cycle determined by compare match set with 64-bit transfer during a crest interrupt and updated at the next trough with fixed buffer operation. |
| General > Period | Value must be a non-negative integer less than or equal to 0x40000000000 | 0x100000000 | Specify the timer period in units selected below. Set the period to 0x100000000 (32-bit) raw counts for a free running timer or an input capture configuration. The period can be set up to 0x40000000000 (32-bit) which will use a divider of 1024 with the maximum period. If the requested period cannot be achieved, the settings with the largest possible period that is less than or equal to the requested period are used. The theoretical calculated period is printed in a comment in the generated timer_cfg_t structure. |
| General > Period Unit |
| Raw Counts | Unit of the period specified above |
| Output > Custom Waveform > GTIOA > Initial Output Level |
| Pin Level Low | Set the initial output level of GTIOCxA. |
| Output > Custom Waveform > GTIOA > Cycle End Output Level |
| Pin Level Retain | Set the output level of GTIOCxA at cycle end. |
| Output > Custom Waveform > GTIOA > Compare Match Output Level |
| Pin Level Retain | Set the output level of GTIOCxA at compare match. |
| Output > Custom Waveform > GTIOA > Retain Output Level at Count Stop |
| Disabled | Retain the current GTIOxA output level when counting is stopped. |
| Output > Custom Waveform > GTIOB > Initial Output Level |
| Pin Level Low | Set the initial output level of GTIOCxB. |
| Output > Custom Waveform > GTIOB > Cycle End Output Level |
| Pin Level Retain | Set the output level of GTIOCxB at cycle end. |
| Output > Custom Waveform > GTIOB > Compare Match Output Level |
| Pin Level Retain | Set the output level of GTIOCxB at compare match. |
| Output > Custom Waveform > GTIOB > Retain Output Level at Count Stop |
| Disabled | Retain the current GTIOxB output level when counting is stopped. |
| Output > Custom Waveform > Custom Waveform Enable |
| Disabled | Enable custom waveform configuration. |
| Output > Duty Cycle Percent (only applicable in PWM mode) | Value must be between 0 and 100 | 50 | Specify the timer duty cycle percent. Only used in PWM mode. |
| Output > GTIOCA Output Enabled |
| False | Enable the output of GTIOCA on a pin. |
| Output > GTIOCA Stop Level |
| Pin Level Low | Select the behavior of the output pin when the timer is stopped. |
| Output > GTIOCB Output Enabled |
| False | Enable the output of GTIOCB on a pin. |
| Output > GTIOCB Stop Level |
| Pin Level Low | Select the behavior of the output pin when the timer is stopped. |
| Input > Count Up Source | MCU Specific Options | Select external source that will increment the counter. If any count up source is selected, the timer will count the external sources only. It will not count PCLKD cycles. | |
| Input > Count Down Source | MCU Specific Options | Select external source that will decrement the counter. If any count down source is selected, the timer will count the external sources only. It will not count PCLKD cycles. | |
| Input > Phase Count Setting Automatically Enable |
| Disabled | Enable Phase Count Setting Automatically. |
| Input > Counting Mode |
| Mode1 | Phase count mode is count up or down operation mode by detecting the phase difference between the inputs on the GTIOCnA and GTIOCnB pins. |
| Input > Start Source | MCU Specific Options | Select external source that will start the timer. For pulse width measurement, set the Start Source and the Clear Source to the trigger edge (the edge to start the measurement), and set the Stop Source and Capture Source (either A or B) to the opposite edge (the edge to stop the measurement). For pulse period measurement, set the Start Source, the Clear Source, and the Capture Source (either A or B) to the trigger edge (the edge to start the measurement). | |
| Input > Stop Source | MCU Specific Options | Select external source that will stop the timer. | |
| Input > Clear Source | MCU Specific Options | Select external source that will clear the timer. | |
| Input > Capture A Source | MCU Specific Options | Select external source that will trigger a capture A event. | |
| Input > Capture B Source | MCU Specific Options | Select external source that will trigger a capture B event. | |
| Input > Noise Filter A Sampling Clock Select |
| No Filter | Select the input filter for GTIOCA. |
| Input > Noise Filter B Sampling Clock Select |
| No Filter | Select the input filter for GTIOCB. |
| Interrupts > Callback | Name must be a valid C symbol | NULL | A user callback function can be specified here. If this callback function is provided, it will be called from the interrupt service routine (ISR) each time the timer period elapses |
| Interrupts > Overflow/Crest Interrupt Priority | MCU Specific Options | Select the overflow interrupt priority. This is the crest interrupt for triangle-wave PWM. | |
| Interrupts > Capture/Compare match A Interrupt Priority | MCU Specific Options | Select the interrupt priority for Capture/Compare match A. | |
| Interrupts > Capture/Compare match B Interrupt Priority | MCU Specific Options | Select the interrupt priority for Capture/Compare match B. | |
| Interrupts > Underflow/Trough Interrupt Priority | MCU Specific Options | Select the interrupt priority for the trough interrupt (triangle-wave PWM only). | |
| Interrupts > Dead Time Error Interrupt Priority | MCU Specific Options | Select the interrupt priority for dead time error. | |
| Interrupts (GPT_SEL) > Callback | Name must be a valid C symbol | NULL | A user callback function can be specified here. If this callback function is provided, it will be called from the interrupt service routine (ISR) each time the timer period elapses |
| Interrupts (GPT_SEL) > Overflow/Crest Interrupt Source | MCU Specific Options | Select the overflow interrupt source. This is the crest interrupt for triangle-wave PWM. | |
| Interrupts (GPT_SEL) > Capture/Compare match A Interrupt Source | MCU Specific Options | Select the interrupt source for Capture/Compare match A. | |
| Interrupts (GPT_SEL) > Capture/Compare match B Interrupt Source | MCU Specific Options | Select the interrupt source for Capture/Compare match B. | |
| Interrupts (GPT_SEL) > Underflow/Trough Interrupt Source | MCU Specific Options | Select the interrupt source for the trough interrupt (triangle-wave PWM only). | |
| Interrupts (GPT_SEL) > Dead Time Error Interrupt Source | MCU Specific Options | Select the interrupt source for dead time error. | |
| Interrupts (GPT_SEL) > INT0 Interrupt Priority | MCU Specific Options | Select the interrupt priority for int0. | |
| Interrupts (GPT_SEL) > INT1 Interrupt Priority | MCU Specific Options | Select the interrupt priority for int1. | |
| Interrupts (GPT_SEL) > INT2 Interrupt Priority | MCU Specific Options | Select the interrupt priority for int2. | |
| Interrupts (GPT_SEL) > INT3 Interrupt Priority | MCU Specific Options | Select the interrupt priority for int3. | |
| Interrupts (GPT_SEL) > INT4 Interrupt Priority | MCU Specific Options | Select the interrupt priority for int4. | |
| Extra Features > Output Disable > POEG Link | MCU Specific Options | Select which POEG to link this GPT channel to. | |
| Extra Features > Output Disable > Output Disable POEG Trigger |
| Select which errors send an output disable trigger to POEG. | |
| Extra Features > Output Disable > GTIOCA Disable Setting |
| Disable Prohibited | Select the disable setting for GTIOCA. |
| Extra Features > Output Disable > GTIOCB Disable Setting |
| Disable Prohibited | Select the disable setting for GTIOCB. |
| Extra Features > ADC Trigger > Start Event Trigger |
| Select which A/D converter start request interrupts to generate and at which point in the cycle to generate them. | |
| Extra Features > ADC Trigger > ADC A Compare Match (Raw Counts) | Must be a valid non-negative integer with a maximum configurable value of 4294967295 (0xffffffff). | 0 | Select the compare match value that generates a GPTn AD TRIG A event. |
| Extra Features > ADC Trigger > ADC B Compare Match (Raw Counts) | Must be a valid non-negative integer with a maximum configurable value of 4294967295 (0xffffffff). | 0 | Select the compare match value that generates a GPTn AD TRIG B event. |
| Extra Features > Dead Time > Dead Time Count Up (Raw Counts) | Must be a valid non-negative integer with a maximum configurable value of 4294967295 (0xffffffff). | 0 | Select the dead time to apply during up counting. |
| Extra Features > Dead Time > Dead Time Count Down (Raw Counts) | Must be a valid non-negative integer with a maximum configurable value of 4294967295 (0xffffffff). | 0 | Select the dead time to apply during down counting. |
| Extra Features > Interrupt Skipping > Interrupt to Count |
| None | Select the count source for interrupt skipping. The interrupt skip counter increments after each source event. All crest/overflow and trough/underflow interrupts are skipped when the interrupt skip counter is non-zero. |
| Extra Features > Interrupt Skipping > Interrupt Skip Count |
| 0 | Select the number of interrupts to skip. |
| Extra Features > Interrupt Skipping > Skip ADC Events |
| None | Select ADC events to suppress when the interrupt skip count is not zero. |
| Extra Features > Extended Interrupt Skipping 1 > Interrupt to Count |
| None | Interrupt source to count for interrupt skipping(GTEITC.EIVTC1) |
| Extra Features > Extended Interrupt Skipping 1 > Interrupt Skip Count | Refer to the RZT Configuration tool for available options. | 0 | Number of interrupts to skip between events(GTEITC.EIVTT1) |
| Extra Features > Extended Interrupt Skipping 2 > Interrupt to Count |
| None | Interrupt source to count for interrupt skipping(GTEITC.EIVTC2) |
| Extra Features > Extended Interrupt Skipping 2 > Interrupt Skip Count | Refer to the RZT Configuration tool for available options. | 0 | Number of interrupts to skip between events(GTEITC.EIVTT2) |
| Extra Features > Input Capture Interrupt Extended Skipping Function > Overflow Interrupt |
| None | Extended Skipping Function Select(GTEITLI1.EITLV) |
| Extra Features > Input Capture Interrupt Extended Skipping Function > Underflow Interrupt |
| None | Extended Skipping Function Select(GTEITLI1.EITLU) |
| Extra Features > Input Capture Interrupt Extended Skipping Function > GTADTRA A/D Converter Start Request |
| None | Extended Skipping Function Select(GTEITLI2.EADTAL) |
| Extra Features > Input Capture Interrupt Extended Skipping Function > GTADTRB A/D Converter Start Request |
| None | Extended Skipping Function Select(GTEITLI2.EADTBL) |
| Extra Features > Extra Features |
| Disabled | Select whether to enable extra features on this channel. |
| Extra Features > Input Capture at Count Stop |
| Enabled | Input Capture Operation Select at Count Stop. |
| Extra Features > Input Capture Signal | MCU Specific Options | Input Capture Signal Select. | |
| ELC > LLPP GPT event A > Trigger Source | MCU Specific Options | ELC source that will trigger LLPP GPT event A. | |
| ELC > LLPP GPT event B > Trigger Source | MCU Specific Options | ELC source that will trigger LLPP GPT event B. | |
| ELC > LLPP GPT event C > Trigger Source | MCU Specific Options | ELC source that will trigger LLPP GPT event C. | |
| ELC > LLPP GPT event D > Trigger Source | MCU Specific Options | ELC source that will trigger LLPP GPT event D. | |
| ELC > LLPP GPT event E > Trigger Source | MCU Specific Options | ELC source that will trigger LLPP GPT event E. | |
| ELC > LLPP GPT event F > Trigger Source | MCU Specific Options | ELC source that will trigger LLPP GPT event F. | |
| ELC > LLPP GPT event G > Trigger Source | MCU Specific Options | ELC source that will trigger LLPP GPT event G. | |
| ELC > LLPP GPT event H > Trigger Source | MCU Specific Options | ELC source that will trigger LLPP GPT event H. | |
| ELC > NONSAFTY GPT event A > Trigger Source | MCU Specific Options | ELC source that will trigger NONSAFTY GPT event A. | |
| ELC > NONSAFTY GPT event B > Trigger Source | MCU Specific Options | ELC source that will trigger NONSAFTY GPT event B. | |
| ELC > NONSAFTY GPT event C > Trigger Source | MCU Specific Options | ELC source that will trigger NONSAFTY GPT event C. | |
| ELC > NONSAFTY GPT event D > Trigger Source | MCU Specific Options | ELC source that will trigger NONSAFTY GPT event D. | |
| ELC > NONSAFTY GPT event E > Trigger Source | MCU Specific Options | ELC source that will trigger NONSAFTY GPT event E. | |
| ELC > NONSAFTY GPT event F > Trigger Source | MCU Specific Options | ELC source that will trigger NONSAFTY GPT event F. | |
| ELC > NONSAFTY GPT event G > Trigger Source | MCU Specific Options | ELC source that will trigger NONSAFTY GPT event G. | |
| ELC > NONSAFTY GPT event H > Trigger Source | MCU Specific Options | ELC source that will trigger NONSAFTY GPT event H. |
The GPT clock is based on the PCLKD frequency. You can set the PCLKD frequency using the Clocks tab of the RZ microprocessor Configuration editor or by using the CGC Interface at run-time.
This module can use GTETRGA, GTETRGB, GTETRGC, GTETRGD, GTIOCA and GTIOCB pins as count sources.
This module can use GTIOCA and GTIOCB pins as output pins for periodic or PWM signals.
This module can use GTIOCA and GTIOCB as input pins to measure input signals.
For devices without units, each of the three groups(LLPP, NONSAFETY, and SAFETY) is treated as a unit in FSP. The correspondence of unit and channel numbers in hardware and FSP Configuration is shown below.
| Device | HW Units (Group) | HW Channels (Group) | (Unit, Channel) in FSP Cofiguration |
|---|---|---|---|
| RZ/T2M | N/A | 0 to 6 (LLPP) 7 to 13 (NONSAFETY) 14 to 17 (SAFETY) | (0, 0) to (0, 6) (1, 0) to (1, 6) (2, 0) to (2, 3) |
| RZ/T2ME | N/A | 0 to 6 (LLPP) 7 to 13 (NONSAFETY) 14 to 17 (SAFETY) | (0, 0) to (0, 6) (1, 0) to (1, 6) (2, 0) to (2, 3) |
| RZ/T2L | N/A | 0 to 6 (LLPP) 7 to 13 (NONSAFETY) 14 to 17 (SAFETY) | (0, 0) to (0, 6) (1, 0) to (1, 6) (2, 0) to (2, 3) |
| RZ/T2H | 0 to 5 (LLPP0) 6 to 8 (LLPP1) 9 (NONSAFETY) 10 (SAFETY) | 0 to 4 (LLPP0) 0 to 4 (LLPP1) 0 to 6 (NONSAFETY) 0 to 3 (SAFETY) | (0, 0) to (5, 4) (6, 0) to (8, 4) (9, 0) to (9, 6) (10, 0) to (10, 3) |
The RZ microprocessor Configuration editor will automatically calculate the period count value and source clock divider based on the selected period time, units and clock speed.
When the selected period unit is "Raw counts", the maximum period setting is 0x40000000000 on a 32-bit timer. This will configure the timer with the maximum period and a count clock divisor of 1024.
The period and duty cycle are updated after the next counter overflow after calling R_GPT_PeriodSet() or R_GPT_DutyCycleSet(). To force them to update before the next counter overflow, call R_GPT_Reset() while the counter is running.
The GPT timer does not support one-shot mode natively. One-shot mode is achieved by stopping the timer in the interrupt service routine before the callback is called. If the interrupt is not serviced before the timer period expires again, the timer generates more than one event. The callback is only called once in this case.
The output waveform in one-shot mode is one PCLK cycle less than the configured period. The configured period must be at least 2 counts to generate an output pulse.
Examples of one-shot signals that can be generated by this module are shown below:
The one-shot pulse mode is an asymmetric PWM mode that provides more control over the rising and falling edges of the output. The user provides a period and initial output level and controls the signal by specifying compare match values for the leading and trailing edges each period.
Examples of PWM signals that can be generated by this module are shown below. The leading and trailing edge match values can be modified using R_GPT_DutyCycleSet() in the overflow interrupt.
If dead time is enabled only match values for GTIOCnA need to be set; the match values for GTIOCnB will be automatically configured in hardware.
The GTIOC pin toggles twice each time the timer expires in periodic mode. This is achieved by defining a PWM wave at a 50 percent duty cycle so that the period of the resulting square wave (from rising edge to rising edge) matches the period of the GPT timer. Since the periodic output is actually a PWM output, the time at the stop level is one cycle shorter than the time opposite the stop level for odd period values.
Examples of periodic signals that can be generated by this module are shown below:
The PWM output signal is high at the beginning of the cycle and low at the end of the cycle.
Examples of PWM signals that can be generated by this module are shown below:
Examples of PWM signals that can be generated by this module are shown below. The duty_cycle_counts can be modified using R_GPT_DutyCycleSet() in the crest interrupt and updated at the following trough for symmetric PWM or modified in both the crest/trough interrupts and updated at the following trough/crest for asymmetric PWM.
Phase count mode is count up or down operation mode by detecting the phase difference between the inputs on the GTIOCnA and GTIOCnB pins. For this operation, configure “Count Up Source” and “Count Down Source” appropriately. Example of setting for phase counting mode 1 are shown below.
| Configuration | Options |
|---|---|
| Input > Phase Count Setting Automatically Enable | - Disabled |
| Input > Count Up Source | - GTIOCA Rising Edge While GTIOCB Low - GTIOCA Falling Edge While GTIOCB High - GTIOCB Rising Edge While GTIOCA High - GTIOCB Falling Edge While GTIOCA Low |
| Count > Count Down Source | - GTIOCA Rising Edge While GTIOCB High - GTIOCA Falling Edge While GTIOCB Low - GTIOCB Rising Edge While GTIOCA Low - GTIOCB Falling Edge While GTIOCA High |
| Configuration | Options |
|---|---|
| Input > Phase Count Setting Automatically Enable | - Enabled |
| Input > Counting Mode | - Mode1 |
Event counting can be done by selecting up or down counting sources from GTETRG pins, ELC events, or GTIOC pins. In event counting mode, the GPT counter is not affected by PCLK.
If the capture edge occurs before the start edge in pulse measurement, the first capture is invalid (0).
The GPT timer can be configured to stop, start, clear, count up, or count down when a GTETRG rising or falling edge occurs.
The GPT timer can be configured to stop, start, clear, count up, or count down when an ELC event occurs.
The GPT timer can trigger the start of other peripherals. The Event Link Controller (r_elc) guide provides a list of all available peripherals.
R_GPT_Enable() must be called when external sources are used for start, stop, clear, or capture.
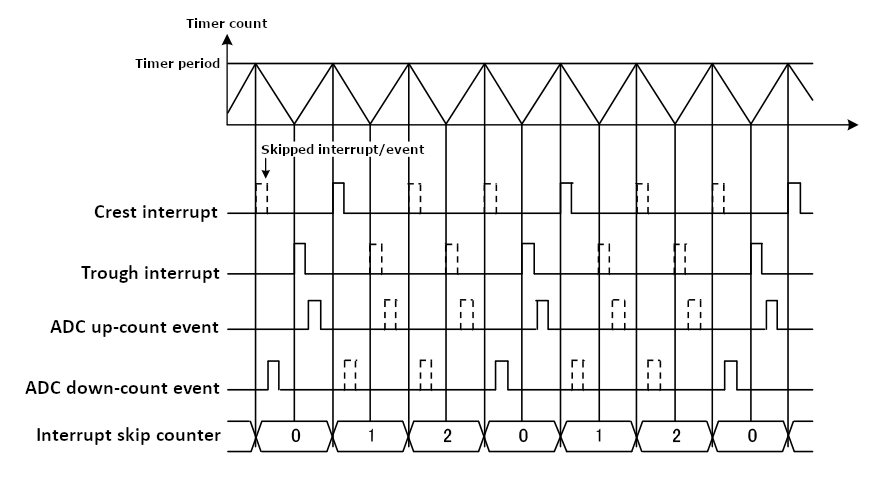
When an interrupt skipping source is selected a hardware counter will increment each time the selected event occurs. Each interrupt past the first (up to the specified skip count) will be suppressed. If ADC events are selected for skipping they will also be suppressed except during the timer period leading to the selected interrupt skipping event (see below diagram).
By using the Custom Waveform option the output pins can be made to output complementary waveforms. To ensure these waveforms stay in sync, the duty cycle for both pins can be set simultaneously by calling R_GPT_DutyCycleSet once with a pin parameter of GPT_IO_PIN_GTIOCA_AND_GTIOCB.
This is a basic example of minimal use of the GPT in an application.
This is an example of a timer callback.
To use the GPT as a free running counter, select periodic mode and set the the Period to 0xFFFFFFFF for a 32-bit timer.
This is an example of using the GPT to capture pulse width or pulse period measurements.
This an example of updating the period.
This an example of updating the duty cycle.
This is an example of using the GPT to start the ADC at a configurable A/D converter compare match value.
This example demonstrates the configuration and use of one-shot pulse mode with GPT timer.
This is an example of using the GPT to operate phase counting mode.
This example demonstrates the configuration and use of compare match with GPT timer.
Data Structures | |
| struct | gpt_output_pin_t |
| struct | gpt_gtior_setting_t |
| struct | gpt_instance_ctrl_t |
| struct | gpt_extended_pwm_cfg_t |
| struct | gpt_extended_cfg_t |
Enumerations | |
| enum | gpt_io_pin_t |
| enum | gpt_buffer_force_push_t |
| enum | gpt_pin_level_t |
| enum | gpt_source_t |
| enum | gpt_capture_filter_t |
| enum | gpt_adc_trigger_t |
| enum | gpt_poeg_link_t |
| enum | gpt_output_disable_t |
| enum | gpt_gtioc_disable_t |
| enum | gpt_adc_compare_match_t |
| enum | gpt_interrupt_skip_source_t |
| enum | gpt_interrupt_skip_count_t |
| enum | gpt_interrupt_skip_adc_t |
| enum | gpt_interrupt_skip_select_t |
| struct gpt_output_pin_t |
Configurations for output pins.
| Data Fields | ||
|---|---|---|
| bool | output_enabled | Set to true to enable output, false to disable output. |
| gpt_pin_level_t | stop_level | Select a stop level from gpt_pin_level_t. |
| struct gpt_gtior_setting_t |
Custom GTIOR settings used for configuring GTIOCxA and GTIOCxB pins.
| struct gpt_instance_ctrl_t |
Channel control block. DO NOT INITIALIZE. Initialization occurs when timer_api_t::open is called.
| struct gpt_extended_pwm_cfg_t |
GPT extension for advanced PWM features.
| Data Fields | ||
|---|---|---|
| uint8_t | trough_ipl | Trough interrupt priority. |
| IRQn_Type | trough_irq | Trough interrupt. |
| gpt_poeg_link_t | poeg_link | Select which POEG channel controls output disable for this GPT channel. |
| gpt_output_disable_t | output_disable | Select which trigger sources request output disable from POEG. |
| gpt_adc_trigger_t | adc_trigger | Select trigger sources to start A/D conversion. |
| uint32_t | dead_time_count_up | Set a dead time value for counting up. |
| uint32_t | dead_time_count_down | Set a dead time value for counting down. |
| uint32_t | adc_a_compare_match | Select the compare match value used to trigger an A/D conversion start request using ELC_EVENT_GPT<channel>_AD_TRIG_A. |
| uint32_t | adc_b_compare_match | Select the compare match value used to trigger an A/D conversion start request using ELC_EVENT_GPT<channel>_AD_TRIG_B. |
| gpt_interrupt_skip_source_t | interrupt_skip_source | Interrupt source to count for interrupt skipping. |
| gpt_interrupt_skip_count_t | interrupt_skip_count | Number of interrupts to skip between events. |
| gpt_interrupt_skip_adc_t | interrupt_skip_adc | ADC events to skip when interrupt skipping is enabled. |
| gpt_interrupt_skip_source_t | interrupt_skip_source_ext1 | Interrupt source to count for interrupt skipping(GTEITC.EIVTC1) |
| gpt_interrupt_skip_count_t | interrupt_skip_count_ext1 | Number of interrupts to skip between events(GTEITC.EIVTT1) |
| gpt_interrupt_skip_source_t | interrupt_skip_source_ext2 | Interrupt source to count for interrupt skipping(GTEITC.EIVTC2) |
| gpt_interrupt_skip_count_t | interrupt_skip_count_ext2 | Number of interrupts to skip between events(GTEITC.EIVTT2) |
| gpt_interrupt_skip_select_t | interrupt_skip_func_ovf | Extended Skipping Function Select(GTEITL1.EITVL) |
| gpt_interrupt_skip_select_t | interrupt_skip_func_unf | Extended Skipping Function Select(GTEITL1.EITUL) |
| gpt_interrupt_skip_select_t | interrupt_skip_func_adc_a | Extended Skipping Function Select(GTEITL2.EADTAL) |
| gpt_interrupt_skip_select_t | interrupt_skip_func_adc_b | Extended Skipping Function Select(GTEITL2.EADTBL) |
| gpt_gtioc_disable_t | gtioca_disable_setting | Select how to configure GTIOCA when output is disabled. |
| gpt_gtioc_disable_t | gtiocb_disable_setting | Select how to configure GTIOCB when output is disabled. |
| struct gpt_extended_cfg_t |
GPT extension configures the output pins for GPT.
| Data Fields | ||
|---|---|---|
| gpt_output_pin_t | gtioca | Configuration for GPT I/O pin A. |
| gpt_output_pin_t | gtiocb | Configuration for GPT I/O pin B. |
| gpt_source_t | start_source | Event sources that trigger the timer to start. |
| gpt_source_t | stop_source | Event sources that trigger the timer to stop. |
| gpt_source_t | clear_source | Event sources that trigger the timer to clear. |
| gpt_source_t | capture_a_source | Event sources that trigger capture of GTIOCA. |
| gpt_source_t | capture_b_source | Event sources that trigger capture of GTIOCB. |
| gpt_source_t | count_up_source |
Event sources that trigger a single up count. If GPT_SOURCE_NONE is selected for both count_up_source and count_down_source, then the timer count source is PCLK. |
| gpt_source_t | count_down_source |
Event sources that trigger a single down count. If GPT_SOURCE_NONE is selected for both count_up_source and count_down_source, then the timer count source is PCLK. |
| gpt_capture_filter_t | capture_filter_gtioca | Debounce filter for GTIOCxA input signal pin. |
| gpt_capture_filter_t | capture_filter_gtiocb | Debounce filter for GTIOCxB input signal pin. |
| uint8_t | capture_a_ipl | Capture A interrupt priority. |
| uint8_t | capture_b_ipl | Capture B interrupt priority. |
| uint8_t | dead_time_ipl | Dead time error interrupt priority. |
| uint8_t | icds | Input Capture Operation Select at Count Stop. |
| IRQn_Type | capture_a_irq | Capture A interrupt. |
| IRQn_Type | capture_b_irq | Capture B interrupt. |
| uint32_t | compare_match_value[2] | Storing compare match value for channels. |
| uint8_t | compare_match_status | Storing the compare match register status. |
| IRQn_Type | dead_time_irq | Dead time error interrupt. |
| gpt_extended_pwm_cfg_t const * | p_pwm_cfg | Advanced PWM features, optional. |
| uint8_t | capture_a_source_select | Capture A interrupt source select. |
| uint8_t | capture_b_source_select | Capture B interrupt source select. |
| uint8_t | cycle_end_source_select | Cycle end interrupt source select. |
| uint8_t | dead_time_error_source_select | Dead time error interrupt source select. |
| uint8_t | trough_source_select | Trough interrupt source select. |
| gpt_gtior_setting_t | gtior_setting | Custom GTIOR settings used for configuring GTIOCxA and GTIOCxB pins. |
| void * | p_reg | Register base address for specified channel. |
| enum gpt_io_pin_t |
Input/Output pins, used to select which duty cycle to update in R_GPT_DutyCycleSet().
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| GPT_IO_PIN_GTIOCA | GTIOCA. |
| GPT_IO_PIN_GTIOCB | GTIOCB. |
| GPT_IO_PIN_GTIOCA_AND_GTIOCB | GTIOCA and GTIOCB. |
| GPT_IO_PIN_TROUGH | Used in R_GPT_DutyCycleSet when Triangle-wave PWM Mode 3 is selected. |
| GPT_IO_PIN_CREST | Used in R_GPT_DutyCycleSet when Triangle-wave PWM Mode 3 is selected. |
| GPT_IO_PIN_ONE_SHOT_LEADING_EDGE | Used in R_GPT_DutyCycleSet to set GTCCRC and GTCCRE registers when One-Shot Pulse mode is selected. |
| GPT_IO_PIN_ONE_SHOT_TRAILING_EDGE | Used in R_GPT_DutyCycleSet to set GTCCRD and GTCCRF registers when One-Shot Pulse mode is selected. |
Forced buffer push operation used in One-Shot Pulse mode with R_GPT_DutyCycleSet().
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| GPT_BUFFER_FORCE_PUSH | Used in R_GPT_DutyCycleSet to force push the data from GTCCRn registers to temporary buffer A or B when One-Shot Pulse mode is selected. |
| enum gpt_pin_level_t |
| enum gpt_source_t |
Sources can be used to start the timer, stop the timer, count up, or count down. These enumerations represent a bitmask. Multiple sources can be ORed together.
| enum gpt_capture_filter_t |
Input capture signal noise filter (debounce) setting. Only available for input signals GTIOCxA and GTIOCxB. The noise filter samples the external signal at intervals of the PCLK divided by one of the values. When 3 consecutive samples are at the same level (high or low), then that level is passed on as the observed state of the signal. See "Noise Filter Function" in the hardware manual, GPT section.
| enum gpt_adc_trigger_t |
Trigger options to start A/D conversion.
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| GPT_ADC_TRIGGER_NONE | None - no output disable request. |
| GPT_ADC_TRIGGER_UP_COUNT_START_ADC_A | Request A/D conversion from ADC unit 0 at up counting compare match of gpt_extended_pwm_cfg_t::adc_a_compare_match. |
| GPT_ADC_TRIGGER_DOWN_COUNT_START_ADC_A | Request A/D conversion from ADC unit 0 at down counting compare match of gpt_extended_pwm_cfg_t::adc_a_compare_match. |
| GPT_ADC_TRIGGER_UP_COUNT_START_ADC_B | Request A/D conversion from ADC unit 1 at up counting compare match of gpt_extended_pwm_cfg_t::adc_b_compare_match. |
| GPT_ADC_TRIGGER_DOWN_COUNT_START_ADC_B | Request A/D conversion from ADC unit 1 at down counting compare match of gpt_extended_pwm_cfg_t::adc_b_compare_match. |
| enum gpt_poeg_link_t |
POEG channel to link to this channel.
| enum gpt_output_disable_t |
Select trigger to send output disable request to POEG.
| enum gpt_gtioc_disable_t |
Disable level options for GTIOC pins.
Interrupt skipping modes
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| GPT_INTERRUPT_SKIP_SOURCE_NONE | Do not skip interrupts. |
| GPT_INTERRUPT_SKIP_SOURCE_OVERFLOW_UNDERFLOW | Count and skip overflow and underflow interrupts. |
| GPT_INTERRUPT_SKIP_SOURCE_CREST | Count crest interrupts for interrupt skipping. Skip the number of crest and trough interrupts configured in gpt_interrupt_skip_count_t. When the interrupt does fire, the trough interrupt fires before the crest interrupt. |
| GPT_INTERRUPT_SKIP_SOURCE_TROUGH | Count trough interrupts for interrupt skipping. Skip the number of crest and trough interrupts configured in gpt_interrupt_skip_count_t. When the interrupt does fire, the crest interrupt fires before the trough interrupt. |
Number of interrupts to skip between events
extended interrupt skipping
| fsp_err_t R_GPT_Open | ( | timer_ctrl_t *const | p_ctrl, |
| timer_cfg_t const *const | p_cfg | ||
| ) |
Initializes the timer module and applies configurations. Implements timer_api_t::open.
GPT hardware does not support one-shot functionality natively. When using one-shot mode, the timer will be stopped in an ISR after the requested period has elapsed.
The GPT implementation of the general timer can accept a gpt_extended_cfg_t extension parameter.
| FSP_SUCCESS | Initialization was successful and timer has started. |
| FSP_ERR_ASSERTION | A required input pointer is NULL or the source divider is invalid. |
| FSP_ERR_ALREADY_OPEN | Module is already open. |
| FSP_ERR_IRQ_BSP_DISABLED | timer_cfg_t::mode is TIMER_MODE_ONE_SHOT or timer_cfg_t::p_callback is not NULL, but ISR is not enabled. ISR must be enabled to use one-shot mode or callback. |
| FSP_ERR_INVALID_MODE | Triangle wave PWM is only supported if GPT_CFG_OUTPUT_SUPPORT_ENABLE is 2. |
| FSP_ERR_IP_CHANNEL_NOT_PRESENT | The channel requested in the p_cfg parameter is not available on this device. |
| fsp_err_t R_GPT_Stop | ( | timer_ctrl_t *const | p_ctrl | ) |
Stops timer. Implements timer_api_t::stop.
| FSP_SUCCESS | Timer successfully stopped. |
| FSP_ERR_ASSERTION | p_ctrl was NULL. |
| FSP_ERR_NOT_OPEN | The instance is not opened. |
| fsp_err_t R_GPT_Start | ( | timer_ctrl_t *const | p_ctrl | ) |
Starts timer. Implements timer_api_t::start.
| FSP_SUCCESS | Timer successfully started. |
| FSP_ERR_ASSERTION | p_ctrl was NULL. |
| FSP_ERR_NOT_OPEN | The instance is not opened. |
| fsp_err_t R_GPT_Reset | ( | timer_ctrl_t *const | p_ctrl | ) |
Resets the counter value to 0. Implements timer_api_t::reset.
| FSP_SUCCESS | Counter value written successfully. |
| FSP_ERR_ASSERTION | p_ctrl was NULL. |
| FSP_ERR_NOT_OPEN | The instance is not opened. |
| fsp_err_t R_GPT_Enable | ( | timer_ctrl_t *const | p_ctrl | ) |
Enables external event triggers that start, stop, clear, or capture the counter. Implements timer_api_t::enable.
| FSP_SUCCESS | External events successfully enabled. |
| FSP_ERR_ASSERTION | p_ctrl was NULL. |
| FSP_ERR_NOT_OPEN | The instance is not opened. |
| fsp_err_t R_GPT_Disable | ( | timer_ctrl_t *const | p_ctrl | ) |
Disables external event triggers that start, stop, clear, or capture the counter. Implements timer_api_t::disable.
| FSP_SUCCESS | External events successfully disabled. |
| FSP_ERR_ASSERTION | p_ctrl was NULL. |
| FSP_ERR_NOT_OPEN | The instance is not opened. |
| fsp_err_t R_GPT_PeriodSet | ( | timer_ctrl_t *const | p_ctrl, |
| uint32_t const | period_counts | ||
| ) |
Sets period value provided. If the timer is running, the period will be updated after the next counter overflow. If the timer is stopped, this function resets the counter and updates the period. Implements timer_api_t::periodSet.
| FSP_SUCCESS | Period value written successfully. |
| FSP_ERR_ASSERTION | p_ctrl was NULL. |
| FSP_ERR_NOT_OPEN | The instance is not opened. |
| fsp_err_t R_GPT_DutyCycleSet | ( | timer_ctrl_t *const | p_ctrl, |
| uint32_t const | duty_cycle_counts, | ||
| uint32_t const | pin | ||
| ) |
Sets duty cycle on requested pin. Implements timer_api_t::dutyCycleSet.
Duty cycle is updated in the buffer register. The updated duty cycle is reflected after the next cycle end (counter overflow).
| [in] | p_ctrl | Pointer to instance control block. |
| [in] | duty_cycle_counts | Duty cycle to set in counts. |
| [in] | pin | Use gpt_io_pin_t to select GPT_IO_PIN_GTIOCA or GPT_IO_PIN_GTIOCB or GPT_IO_PIN_GTIOCA_AND_GTIOCB. |
| FSP_SUCCESS | Duty cycle updated successfully. |
| FSP_ERR_ASSERTION | p_ctrl was NULL or the pin is not one of gpt_io_pin_t |
| FSP_ERR_NOT_OPEN | The instance is not opened. |
| FSP_ERR_INVALID_ARGUMENT | Duty cycle is larger than period. |
| FSP_ERR_INVALID_MODE | GPT_IO_PIN_TROUGH, and GPT_IO_PIN_CREST settings are invalid in the this mode. |
| FSP_ERR_UNSUPPORTED | GPT_CFG_OUTPUT_SUPPORT_ENABLE is 0. |
| fsp_err_t R_GPT_CompareMatchSet | ( | timer_ctrl_t *const | p_ctrl, |
| uint32_t const | compare_match_value, | ||
| timer_compare_match_t const | match_channel | ||
| ) |
Set value for compare match feature. Implements timer_api_t::compareMatchSet.
Example:
| FSP_SUCCESS | Set the compare match value successfully. |
| FSP_ERR_ASSERTION | p_ctrl was NULL. |
| FSP_ERR_NOT_OPEN | The instance is not opened. |
| FSP_ERR_NOT_ENABLED | Requested compare channel is disabled. |
| fsp_err_t R_GPT_InfoGet | ( | timer_ctrl_t *const | p_ctrl, |
| timer_info_t *const | p_info | ||
| ) |
Get timer information and store it in provided pointer p_info. Implements timer_api_t::infoGet.
| FSP_SUCCESS | Period, count direction, frequency, and ELC event written to caller's structure successfully.(External clock(GTETRGA - GTETRGD) cannot be acquired.) |
| FSP_ERR_ASSERTION | p_ctrl or p_info was NULL. |
| FSP_ERR_NOT_OPEN | The instance is not opened. |
| fsp_err_t R_GPT_StatusGet | ( | timer_ctrl_t *const | p_ctrl, |
| timer_status_t *const | p_status | ||
| ) |
Get current timer status and store it in provided pointer p_status. Implements timer_api_t::statusGet.
| FSP_SUCCESS | Current timer state and counter value set successfully. |
| FSP_ERR_ASSERTION | p_ctrl or p_status was NULL. |
| FSP_ERR_NOT_OPEN | The instance is not opened. |
| fsp_err_t R_GPT_CounterSet | ( | timer_ctrl_t *const | p_ctrl, |
| uint32_t | counter | ||
| ) |
Set counter value.
| FSP_SUCCESS | Counter value updated. |
| FSP_ERR_ASSERTION | p_ctrl or p_status was NULL. |
| FSP_ERR_NOT_OPEN | The instance is not opened. |
| FSP_ERR_IN_USE | The timer is running. Stop the timer before calling this function. |
| fsp_err_t R_GPT_OutputEnable | ( | timer_ctrl_t *const | p_ctrl, |
| gpt_io_pin_t | pin | ||
| ) |
Enable output for GTIOCA and/or GTIOCB.
| FSP_SUCCESS | Output is enabled. |
| FSP_ERR_ASSERTION | p_ctrl or p_status was NULL. |
| FSP_ERR_NOT_OPEN | The instance is not opened. |
| fsp_err_t R_GPT_OutputDisable | ( | timer_ctrl_t *const | p_ctrl, |
| gpt_io_pin_t | pin | ||
| ) |
Disable output for GTIOCA and/or GTIOCB.
| FSP_SUCCESS | Output is disabled. |
| FSP_ERR_ASSERTION | p_ctrl or p_status was NULL. |
| FSP_ERR_NOT_OPEN | The instance is not opened. |
| fsp_err_t R_GPT_AdcTriggerSet | ( | timer_ctrl_t *const | p_ctrl, |
| gpt_adc_compare_match_t | which_compare_match, | ||
| uint32_t | compare_match_value | ||
| ) |
Set A/D converter start request compare match value.
| FSP_SUCCESS | Counter value updated. |
| FSP_ERR_ASSERTION | p_ctrl or p_status was NULL. |
| FSP_ERR_NOT_OPEN | The instance is not opened. |
| fsp_err_t R_GPT_CallbackSet | ( | timer_ctrl_t *const | p_ctrl, |
| void(*)(timer_callback_args_t *) | p_callback, | ||
| void const *const | p_context, | ||
| timer_callback_args_t *const | p_callback_memory | ||
| ) |
Updates the user callback with the option to provide memory for the callback argument structure. Implements timer_api_t::callbackSet.
| FSP_SUCCESS | Callback updated successfully. |
| FSP_ERR_ASSERTION | A required pointer is NULL. |
| FSP_ERR_NOT_OPEN | The control block has not been opened. |
| fsp_err_t R_GPT_Close | ( | timer_ctrl_t *const | p_ctrl | ) |
Stops counter, disables output pins, and clears internal driver data. Implements timer_api_t::close.
| FSP_SUCCESS | Successful close. |
| FSP_ERR_ASSERTION | p_ctrl was NULL. |
| FSP_ERR_NOT_OPEN | The instance is not opened. |